VTP (Virtual Trunking Protocol) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that maintains VLAN configuration consistency by managing the addition, deletion, and renaming of VLANs on a network.
Devices that are connected to the same VTP domain share VLAN information so that they can communicate with each other. VTP reduces administration costs and ensures consistency across the network.
VTP works by creating a VLAN database on a VTP server and distributing it to VTP clients. When a change is made to the VLAN database on the server, the changes are propagated to all of the clients.
The clients then update their own VLAN databases to match the servers. This process ensures that all devices in the VTP domain have the same VLAN information.
VTP is a layer 2 protocol that uses trunking to carry VLAN information between devices. Trunking is a technique for bundling multiple logical links into a single physical link. This allows more efficient use of bandwidth and reduces the amount of cabling required.
VTP is available in three different versions: Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3. Version 1 is the original version of VTP and is no longer supported by Cisco. Version 2 was introduced in IOS 12.0(5)T and added support for private VLANs. Version 3 was introduced in IOS 12.2(25)EWA and added support for Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP).
VTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol and is not compatible with other vendors’ equipment.
VTP States
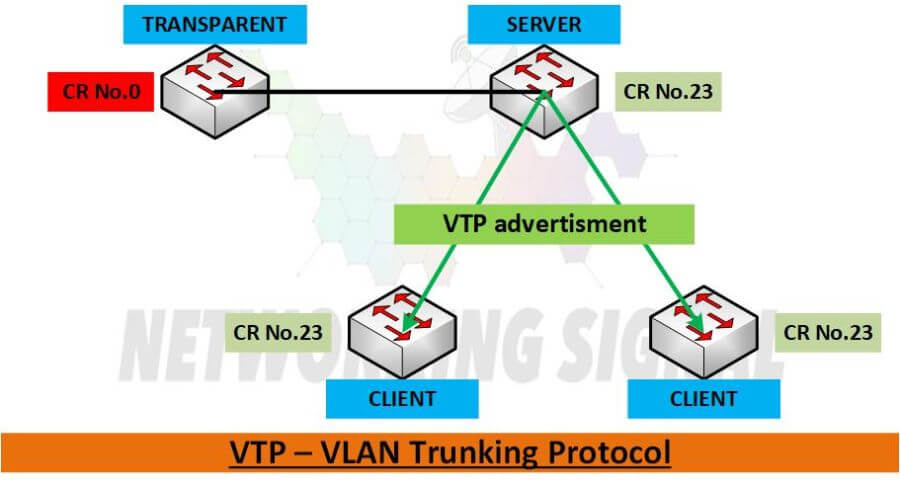
There are three VTP states: server, client, and transparent.
Server: The VTP server is the center of the VTP domain. It is responsible for creating, modifying, and distributing the VLAN database to all of the clients in the domain. The server state is the only state where changes to the VLAN database are allowed.
Client: The VTP client is a device that receives and stores the VLAN database from the server. It cannot make any changes to the database. The client state is useful for devices that need to be aware of the VLANs on the network but does not need to participate in their creation or management.
Transparent: The transparent state is a special state that allows a device to forward VTP information without participating in the VTP process. Transparent mode is useful for devices that need to participate in VLANs but cannot or should not participate in the VTP process.
- For example, a device that is connected to two different networks may need to be able to send and receive VTP information from both networks. In this case, the device would be configured as a transparent mode gateway.
What is VTP Message?
A VTP message is a data packet that contains information about the VLANs on a network. VTP messages are sent between devices in order to keep the VLAN configuration consistent across the network.
VTP messages are sent using the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP). CDP is a layer 2 protocol that is used to discover other Cisco devices on a network. CDP is a part of the VTP protocol and is used to transport VTP messages between devices.
What is VTP Domain?
A VTP domain is a collection of devices that share the same VLAN information. A VTP domain can be as small as two devices or as large as the entire network. All devices in a VTP domain must use the same VTP version and have the same VTP domain name.
The VTP domain name is used to identify which devices are part of the domain. The domain name is case-sensitive and can be up to 32 characters long.

