DHCP and DNS are two important network protocols. DHCP is used to automatically assign IP addresses to devices on a network, while DNS is used to resolve domain names into IP addresses.
In order for devices on a network to communicate with each other, they must have unique IP addresses. DHCP makes this process easier by automatically assigning IP addresses to devices as they connect to the network.
DNS resolves domain names into IP addresses so that devices can communicate with each other using human-readable names instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses.
Both DHCP and DNS are essential for proper network functioning, and most networks will use both protocols.
Should DNS and DHCP be on the same server?
It is not necessary for DNS and DHCP to be on the same server, but it can be helpful to have them on the same server if you are managing a small network. Having DNS and DHCP on the same server can make administration easier because you only have to update one server when IP addresses change or when new domains are added.
However, for larger networks, it is generally recommended to have separate DHCP and DNS servers. This can improve performance and security, and it also allows you to more easily update one server without affecting the other.
Can We Configure DNS on Network Devices?
Most network devices, such as routers and switches, can be configured to act as DNS servers. However, it is generally not recommended to use network devices as DNS servers, because they are not designed for this purpose and may not provide the same level of performance or security as dedicated DNS servers.
Can We Configure DHCP on Network Devices?
Yes, DHCP can be configured on network devices such as routers and switches. However, it is generally not recommended to use network devices as DHCP servers, because they are not designed for this purpose and may not provide the same level of performance or security as dedicated DHCP servers.
How Do DNS and DHCP work together?
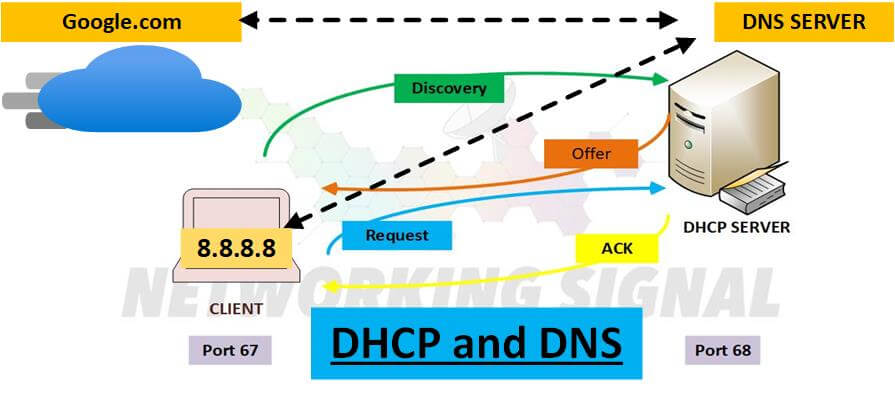
DNS and DHCP work together to provide IP addresses to devices on a network. DNS resolves domain names into IP addresses so that devices can communicate with each other using human-readable names instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses. DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices as they connect to the network.
In order for devices on a network to communicate with each other, they must have unique IP addresses. DHCP makes this process easier by automatically assigning IP addresses to devices as they connect to the network.
DNS resolves domain names into IP addresses so that devices can communicate with each other using human-readable names instead of hard-to-remember IP addresses.
Both DHCP and DNS are essential for proper network functioning, and most networks will use both protocols.