What is Express Route Circuit?
An Express Route circuit is a type of connection that allows you to create a private, high-bandwidth network between your on-premises locations and Azure. Express Route circuits can provide you with more consistent and lower latency than typical internet connections, as well as greater security and reliability.
You can use an Express Route circuit to connect to Azure services, such as Azure Virtual Machines, and to other cloud services, such as Office 365.
Component of Express route circuit
An Express Route circuit consists of the following components:
- A physical connection to an Azure ExpressRoute location. The connection can be provided by one of Azure’s ExpressRoute partners, such as AT&T, Verizon, Equinix, or TelecityGroup.
- An Exchange Provider (EP), is a network service provider that owns and operates the physical connection to Azure. The EP also provides you with a Layer 2 circuit that connects you to the Azure peering location.
- Azure ExpressRoute service, which provides software-defined networking (SDN) capabilities for the circuit.
Features of ExpressRoute Circuit
Some of the key features of an Express Route circuit include:
High bandwidth: ExpressRoute circuits can provide you with up to 10 Gbps of bandwidth.
Low latency and high reliability: ExpressRoute circuits offer more consistent and lower latency than typical internet connections. Azure ExpressRoute also provides you with built-in redundancy, so if one circuit goes down, your connection will still be up and running.
Private connectivity: ExpressRoute circuits provide you with a private connection to Azure, which can help to improve security and reliability.
Flexible and scalable: ExpressRoute circuits are flexible and can be scaled up or down to meet your changing needs.
How to Express Route Circuit work?
Azure ExpressRoute circuits use Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) to exchange routing information with on-premises routers. BGP is a standard protocol that is commonly used by ISPs to exchange routing information.
By using BGP, AzureExpress Route circuits can provide you with more consistent and lower latency than typical internet connections. In addition, BGP can provide you with greater security and reliability because it uses a more sophisticated routing algorithm than the one that is used by typical internet connections.
How to Create Express Route Circuit?
Here are the steps to create an Express Route circuit:
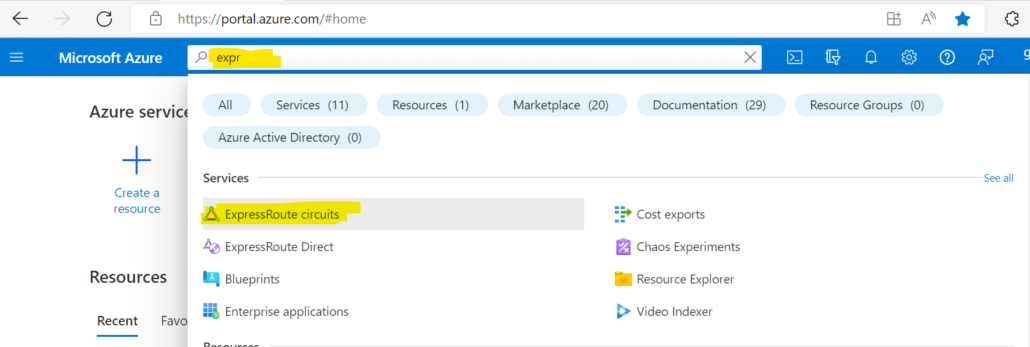
1. Log into the Azure Portal. Search for Express Route Circuit and select ‘Express Route Circuits’.
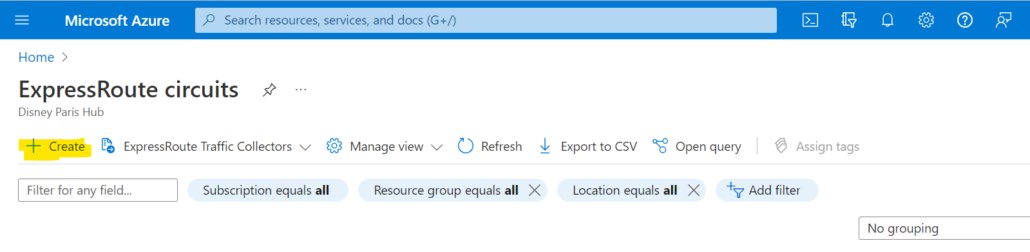
2. Click ‘Add’ to create a new circuit.
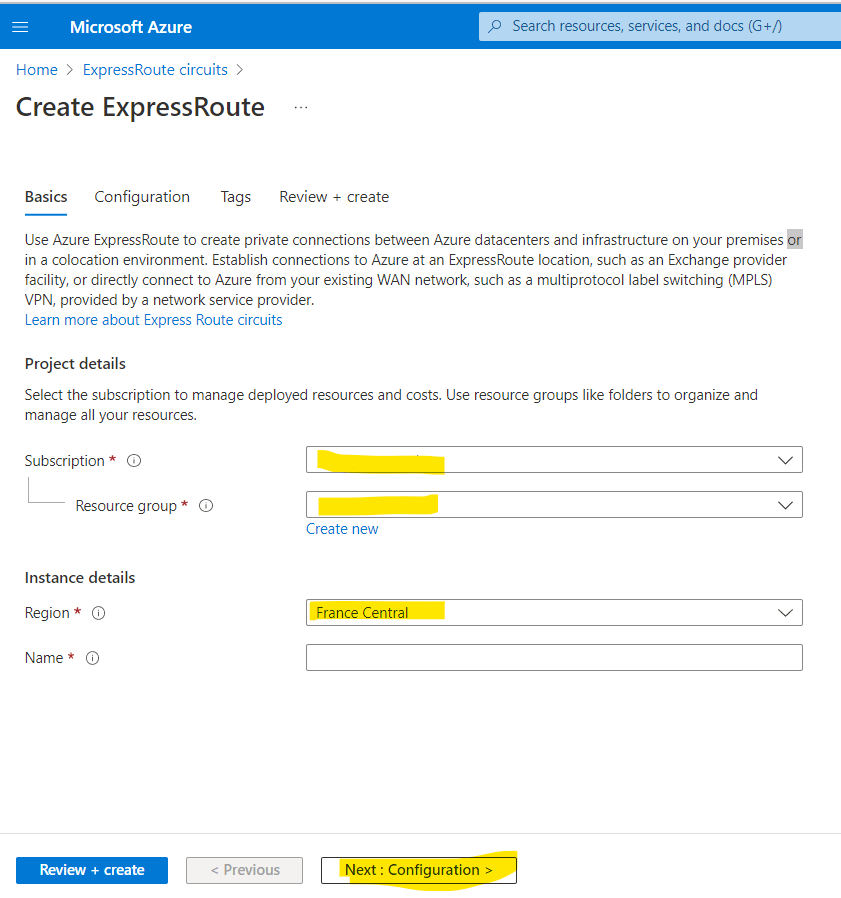
3. Select the resource group you wish to use, or create a new one. Give the circuit a name and select the location.
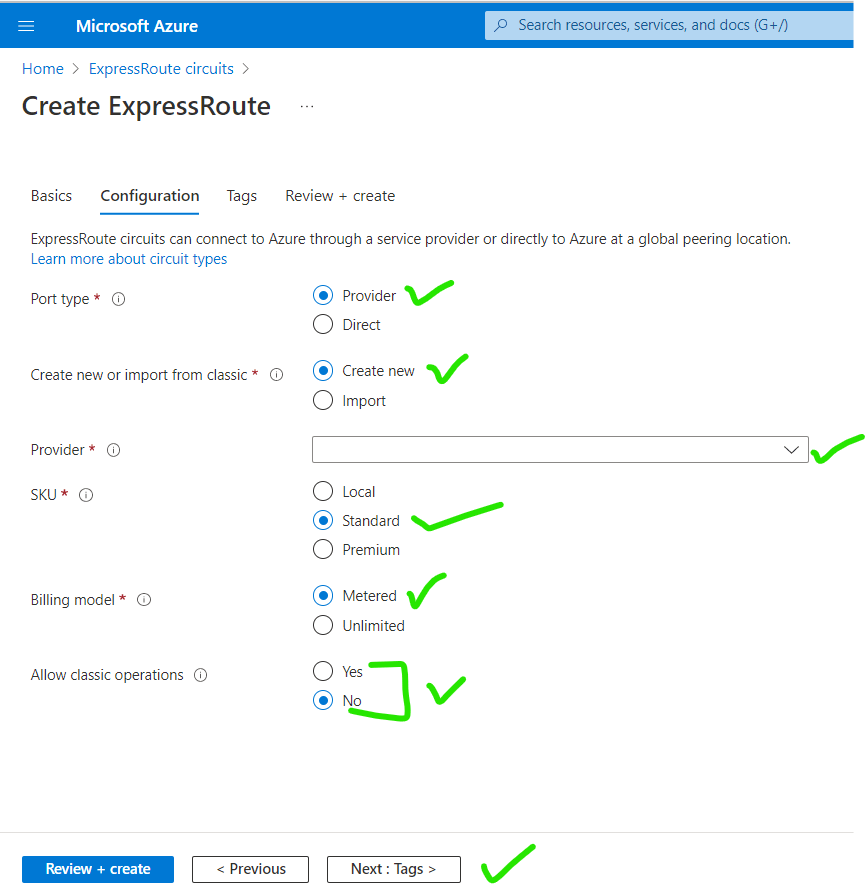
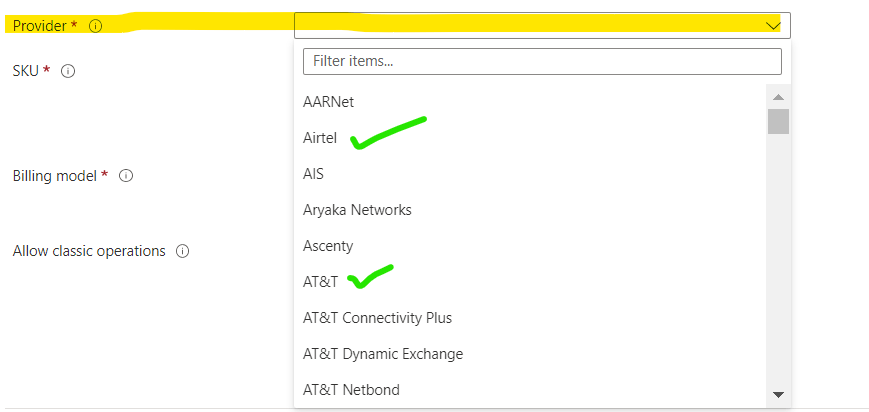
4. Select the Port Type, Provider, SKU, Billing Model, and Operations. Click on Next.
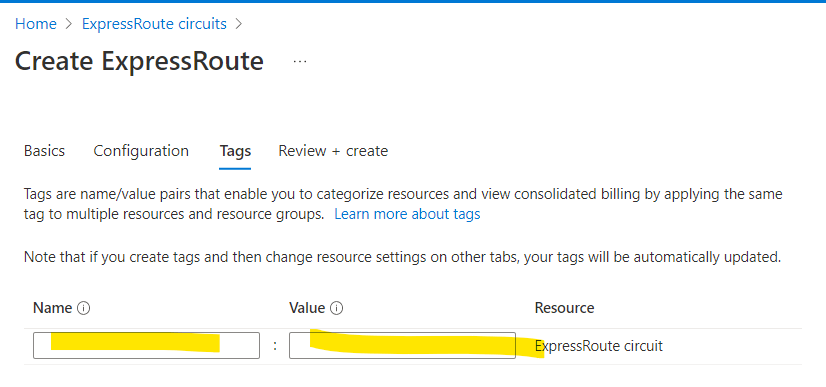
5. Add the Tag according to your needs.
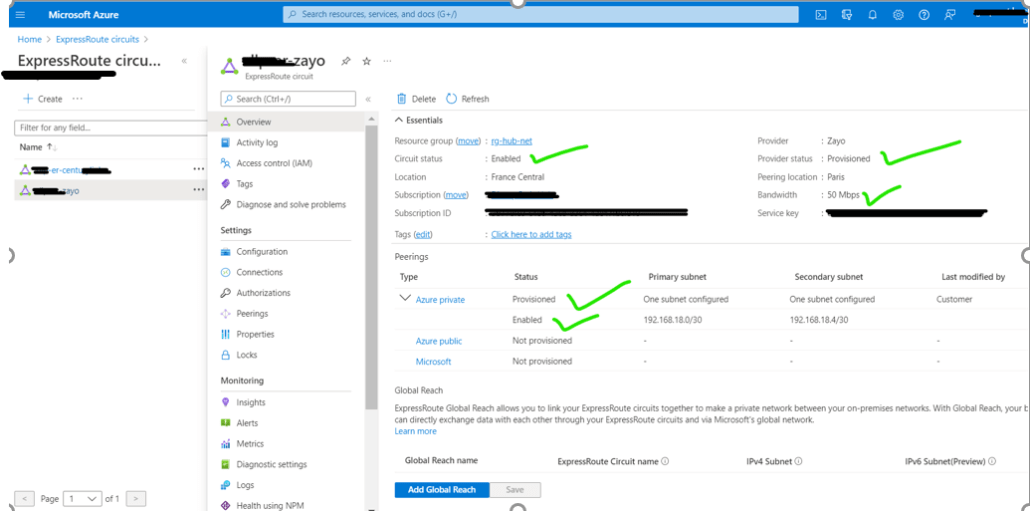
6. Now click on create and your Express Route Circuit has been created. Your new circuit will now be provisioned. You can check its status by going back to the ‘Express Route Circuits page.
Now we are going to establish the connection between the on-premise data center to Azure Cloud.
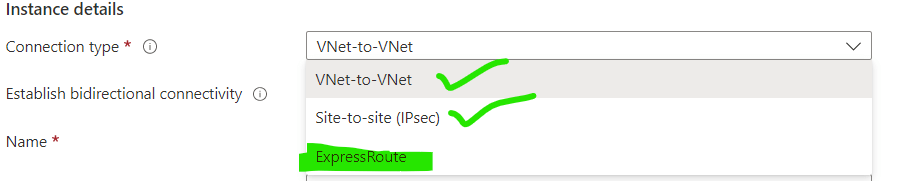
1. Go to your newly created Express Circuit and select Connection. Select the Resource Group, Connection type(select express route), Name, and Region.
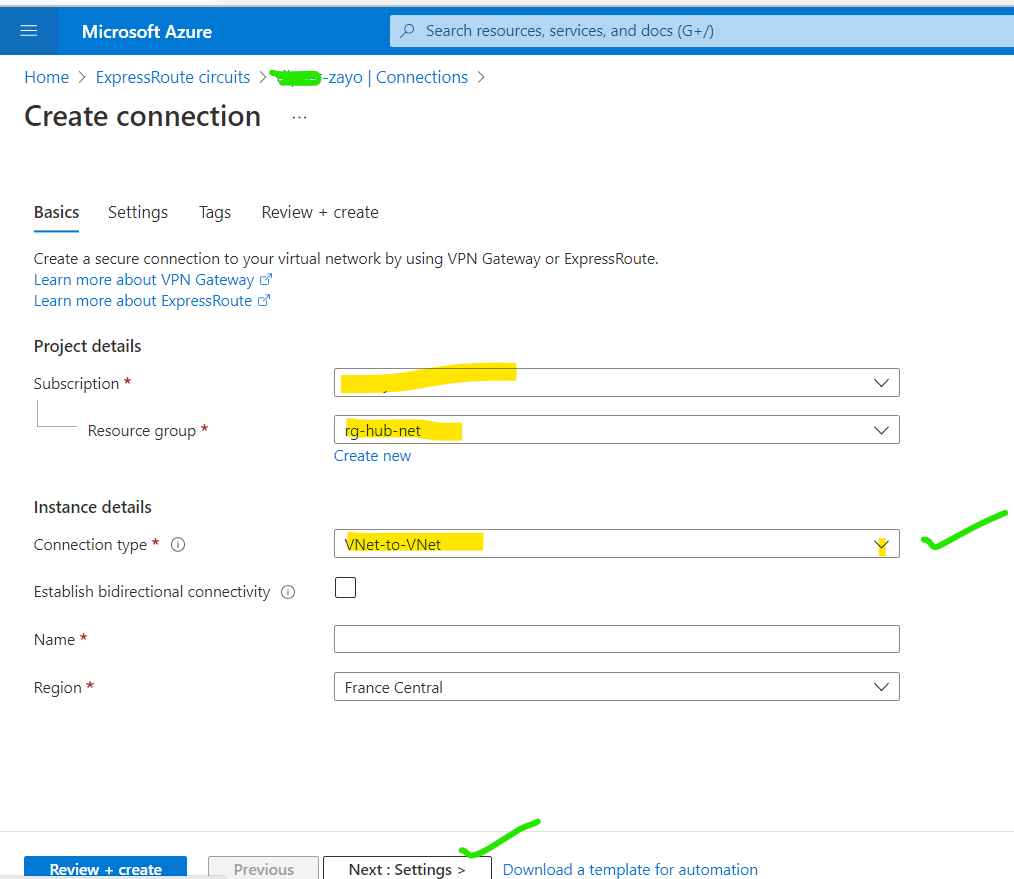
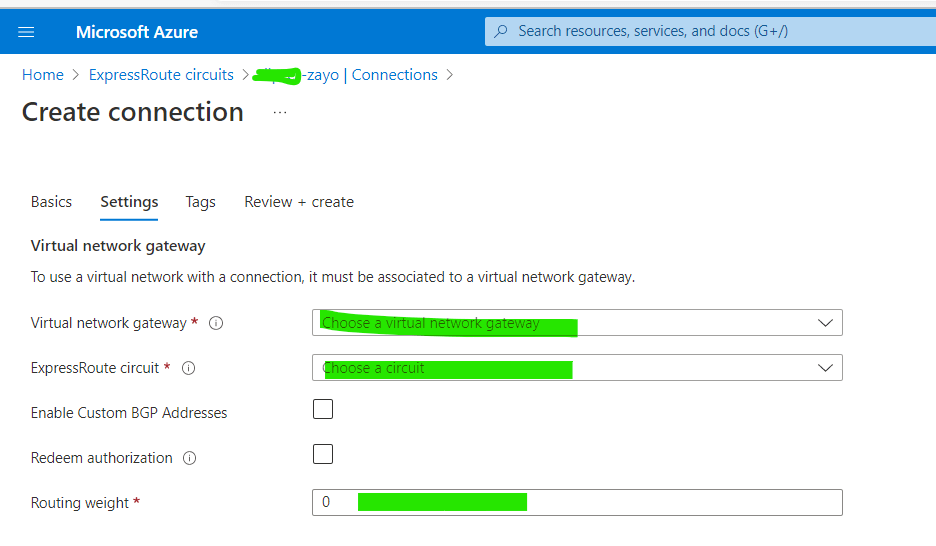
2. Go to the Setting and select the Virtual Gateway and newly Created ExpressRoute Circuit. Enter the routing weight according to your need.
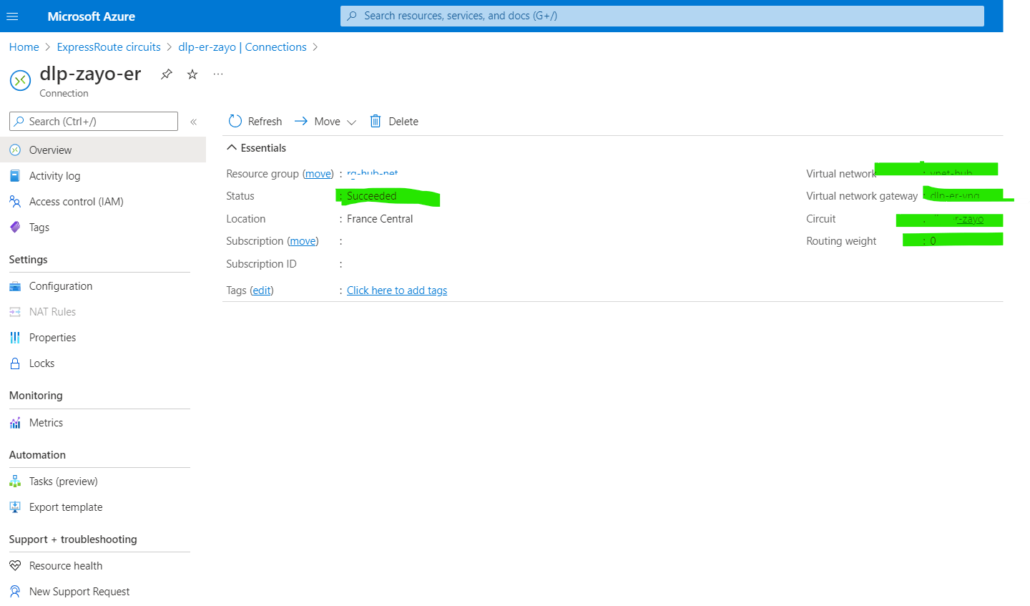
3. Now the Connection has been ready and checks the status of the Connection.
4. Troubleshoot the Express Route Circuit, go to the Logs, and select according to your troubleshooting need.
Advantages of using an Express Route circuit
There are many advantages to using an Express Route circuit, including the following:
- An Express Route circuit can provide you with more consistent and lower latency than typical internet connections.
- An Express Route circuit can provide you with greater security and reliability.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect to Azure services, such as Azure Virtual Machines, and to other cloud services, such as Office 365.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect to Azure through a private peering connection or a public peering connection.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect to Azure through an Exchange Provider (EP) or an Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect to Azure through an on-premises network or a VPN gateway.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect to Azure through an Azure firewall or an Azure Load Balancer.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect multiple on-premises locations to Azure.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect an on-premises data center to Azure.
- An Express Route circuit can be used to connect an on-premises network to Azure through a site-to-site VPN connection.
Relationship between ExpressRoute Circuit and VNet
An Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is a representation of your own network in the cloud. It is logically isolated from other virtual networks in Azure. You have full control over your virtual networking environment, including the selection of your own IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and gateways. An Express Route circuit can be used to connect an Azure VNet to your on-premises network.
When you connect an Azure VNet to an Express Route circuit, the VNet is still logically isolated from other virtual networks in Azure. However, the VNet will have access to all of the resources that are available on the Express Route circuit.
- For example, if you have an Azure VNet that is connected to an Express Route circuit, the VNet will have access to all of the Azure services that are available on the Express Route circuit.
You can connect multiple Azure VNets to an Express Route circuit.
- For example, you could connect an Azure VNet that is used for production workloads to an Express Route circuit, and you could connect an Azure VNet that is used for development workloads to the same Express Route circuit.
Pricing for Express Route circuits
The pricing for Express Route circuits depends on the following factors:
- The size of the circuit.
- The location of the circuit.
- The type of circuit.
- The provider of the circuit.
The price for an Express Route circuit also depends on whether you use a public peering connection or a private peering connection. A public peering connection is less expensive than a private peering connection.