Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a type of data-carrying technique for high-performance telecommunications networks that direct data from one network node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, avoiding complex lookups in a routing table.
The labels identify virtual links (paths) between distant nodes rather than endpoints. MPLS can be used to create a virtual private network (VPN) by dynamically routing packets across the Internet.
MPLS is implemented in software, firmware, or hardware and can be used in conjunction with other networking technologies, such as routers, switches, optical transport systems, security devices, and servers. MPLS works best in networks that have been designed using traffic engineering principles.
See Also: How MPLS Works and How do Labels Forwarding in MPLS?
History of MPLS
MPLS was first proposed in the late 1990s by a team of network engineers at Cisco Systems. The goal was to create a layer 2 switching technology that could be used to improve the performance of IP networks. MPLS was standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in 2004 and has since been adopted by major networking equipment vendors.
What are the Components of MPLS?
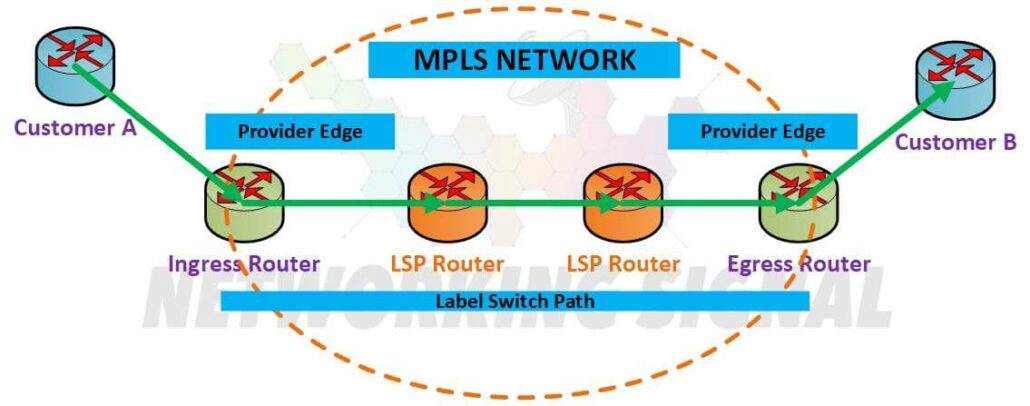
MPLS networks consist of the following components:
Label Edge Routers (LERs): LERs are routers that are located at the edge of an MPLS network. They are responsible for forwarding packets into and out of the MPLS network.
Label Switching Routers (LSRs): LSRs are routers that are located in the core of an MPLS network. They are responsible for forwarding packets between LERs.
Label Switched Paths (LSPs): LSPs are logical paths that are created by LSRs to forward packets between LERs. LSPs can be created statically (by network administrators) or dynamically (by the LSRs themselves).
Labels: Labels are short, fixed-length identifiers that are used by LSRs to forward packets along an LSP. The size of a label (in bits) is determined by the particular MPLS implementation. A label is 4 bytes long in MPLS.
What are the Benefits of MPLS?
MPLS provides many benefits over traditional data-carrying techniques, such as:
Increased bandwidth: MPLS can increase the bandwidth of a network by using short path labels instead of long network addresses. This allows for more efficient use of bandwidth and can result in increased throughput and higher speeds.
Reduced latency: MPLS can reduce latency by using shorter path labels. This allows data to be routed more quickly and can result in lower latency and improved performance.
Improved security: MPLS can improve security by using encryption and other security measures to protect data as it is routed across the network.
Improved reliability: MPLS can improve reliability by using redundancy and other methods to ensure that data is routed correctly even if some part of the network fails.
Improved scalability: MPLS can improve scalability by allowing for more efficient use of bandwidth and by supporting a larger number of virtual private networks (VPNs).
Relationship Between MPLS and SDWAN
Here are the points of the relationship between MPLS and SDWAN:
- MPLS is a Layer 2 switching technology that can be used to improve the performance of IP networks while SDWAN is a Layer 3 network architecture that uses software-defined networking (SDN) to manage and route traffic across multiple Wide Area Networks (WANs).
- MPLS is used to create label-switched paths (LSPs) between network nodes while SDWAN can be used to create virtual private networks (VPNs) across multiple WANs.
- MPLS works best in networks that have been designed using traffic engineering principles while SDWAN can be used in any network architecture.
- MPLS is a standards-based technology that is supported by major networking equipment vendors while SDWAN is an emerging technology with a smaller number of vendors.
- MPLS requires special hardware and software to be implemented while SDWAN can be implemented using standard networking hardware and software.
What is the Importance of MPLS in ISP?
MPLS is important in ISP networks for the following reasons:
- It enables providers to offer a better quality of service (QoS) to their customers by reserving bandwidth for real-time applications such as VoIP and video conferencing.
- It allows providers to offer virtual private networks (VPNs) to their customers. VPNs allow businesses to extend their private networks across the public Internet.
- It enables providers to offer different classes of service to their customers. For example, a provider could offer a premium class of service for business customers that need guaranteed low latency and high throughput.
- It allows providers to manage their network traffic more effectively by using label switching to route traffic along the most efficient path.
- It enables providers to offer new services and applications to their customers by using MPLS-based technologies such as Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs).

