What is Azure Virtual network gateway (VNG)?
A virtual network gateway is a software-based, fully managed multi-tenant gateway that provides secure, connective “bridging” services. Its main purpose is to provide an Azure cloud platform for on-premises and cross-premises connectivity for both virtual networks (VNets) and sites. The Azure virtual network gateway can be used to connect Azure VNets to each other, as well as on-premises locations.
Cross-premises connectivity is an essential part of any hybrid cloud solution. The virtual network gateway provides this by connecting the on-premises network to the Azure virtual network. This connection can be used for a variety of purposes, such as providing access to Azure resources from on-premises or connecting on-premises sites to each other using the Azure virtual network as a transit hub.
The Azure virtual network gateway is a high-performance, highly available gateway that can scale to meet the needs of the largest deployments. It is designed to provide 99.9% availability and can be deployed in multiple Azure regions for added resiliency.
The Azure virtual network gateway supports both policy-based and route-based VPNs. Policy-based VPNs are the simplest to deploy but are limited in that they can only support a single tunnel. Route-based VPNs are more flexible and can support multiple tunnels.
The Azure virtual network gateway supports a variety of networking protocols and technologies, such as:
How do we create an Azure Virtual network gateway?
Here are the steps:
1. Log in to Azure Portal.
2. Search Virtual Network Gateway and Open it.
3. Click on Create for New Virtual Network Gateway.
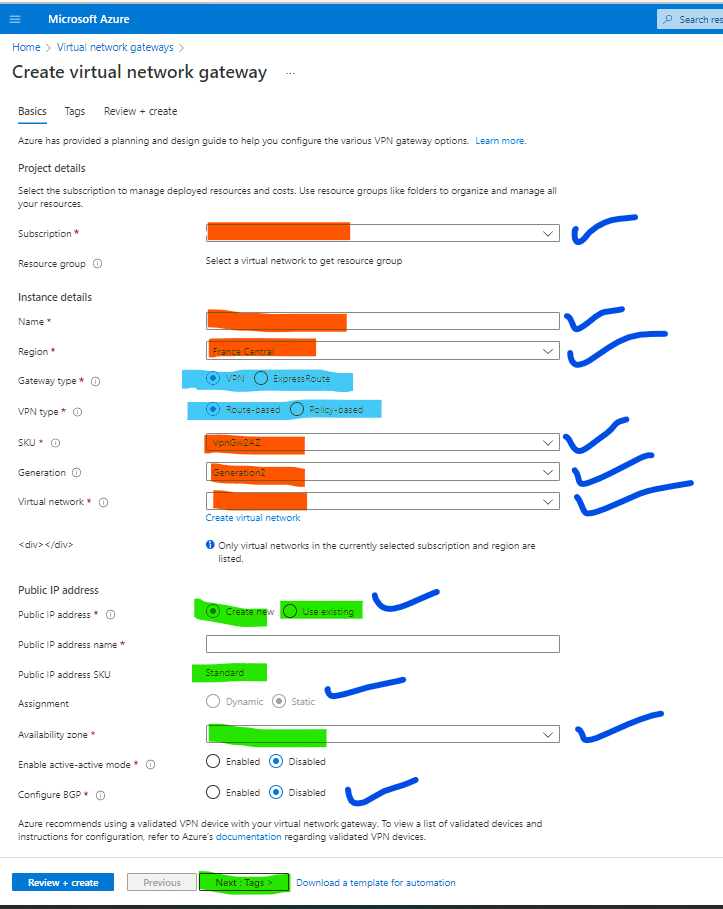
4. Fill required things, subscription, resource group, name, region, VPN type, Vnet, public IP, SKU etc. Click on Next.
5. Do Tagging and click review and create after validating it. Now Virtual Network Gateway is ready to use.
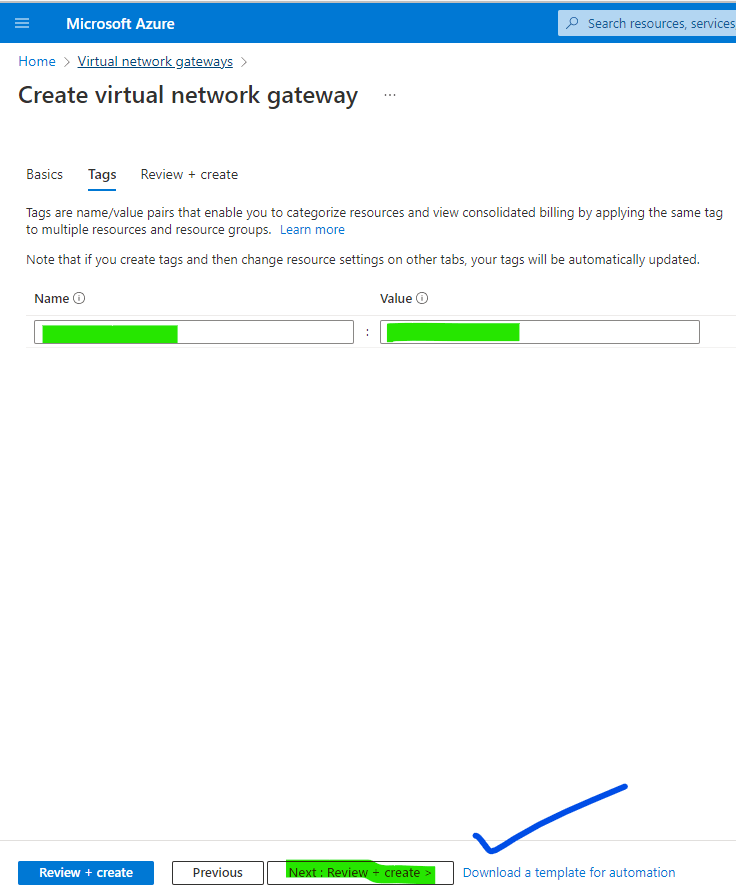
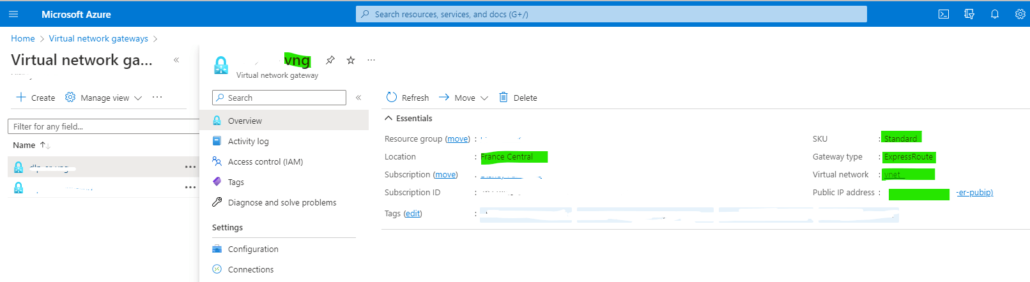
6. Virtual Network Gateway Configured.
Can we create two virtual network gateways in a VNet?
Yes, you can create two virtual network gateways in a Vnet. This will provide you with more flexibility and scalability when connecting your on-premises network to the Azure virtual network. If one gateway goes down, the other will take over and maintain the connection.
How many express routes circuits we can connect with a Virtual network gateway?
You can connect up to 10 ExpressRoute circuits to a virtual network gateway. This will provide you with redundancy and failover in the event that one circuit goes down. Additionally, it will allow you to scale your bandwidth as needed.
Do we need a public IP address for a Virtual network gateway?
Yes, a public IP address is required for a virtual network gateway. This is because the gateway will be communicating with the Azure public cloud.
What are the benefits of using a Virtual network gateway?
The Azure virtual network gateway provides many benefits, including:
Reduced complexity: The Azure virtual network gateway is a fully managed service that can be deployed in minutes. There is no need to deploy and manage hardware or software VPN appliances.
Increased scalability: The Azure virtual network gateway can scale to meet the needs of the largest deployments. It is designed to provide 99.9% availability.
High performance: The Azure virtual network gateway is a high-performance gateway that can provide up to 10 Gbps of throughput.
Flexibility: The Azure virtual network gateway supports both policy-based and route-based VPNs. It also supports a variety of networking protocols and technologies, such as IPsec, IKEv2, SSL/TLS, BGP, and GRE.
Resiliency: The Azure virtual network gateway can be deployed in multiple Azure regions for added resiliency.
What are the limitations of using a Virtual network gateway?
The Azure virtual network gateway has the following limitations:
- Only one active VPN connection can be maintained at a time.
- The maximum number of simultaneous connections is 10.
- The maximum throughput is 10 Gbps.
- The maximum latency is 500 ms.
- The virtual network gateway cannot be deployed in an Availability Zone.
Traffic flow in Virtual Network Gateway
When you deploy a virtual network gateway, two gateway subnets are automatically created for you in the virtual network. These subnets are used by the gateway services and must not be modified or deleted.
Incoming traffic from the on-premises network is routed to the Azure virtual network gateway through the public IP address. The traffic is then encrypted and passed through the Azure VPN gateway to the virtual network. From there, the traffic is routed to the appropriate resource based on the routing table.
Outgoing traffic from the Azure virtual network is routed to the Azure virtual network gateway. The traffic is then passed through the VPN gateway to the on-premises network. From there, the traffic is routed to the appropriate resource based on the routing table.

