What is GRE?
GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is a tunnelling protocol developed by Cisco that allows remote hosts to connect to a private network over the Internet. GRE is often used to connect an on-premises network to a cloud-based virtual private network (VPN).
GRE tunnels can be used to transport IPv4 traffic across an IPv4 or IPv6 network. When transporting IPv4 traffic, GRE uses the IPv4 protocol to encapsulate the original IPv4 packets. When transporting IPv6 traffic, GRE uses the IPv6 protocol to encapsulate the original IPv6 packets.
GRE is a Layer 3 protocol and can be used over any IP-based network. GRE tunnels are point-to-point and do not support multicast traffic.
GRE tunnels are often used to connect an on-premises network to a cloud-based virtual private network (VPN). Cloud-based VPNs can provide a more secure and reliable connection than an on-premises VPN because they are not subject to the same physical security risks.
Benefits of GRE Generic Routing Encapsulation
(GRE) has a number of benefits:
- GRE is a tunnelling protocol that can encapsulate a wide variety of network layer protocols inside virtual point-to-point links over an Internet Protocol network.
- GRE keeps the original IP header intact, which allows the packets to be processed by intermediate routers without inspection or reassembly.
- GRE is a lightweight protocol that does not require additional software or hardware support at the intermediate routers.
- GRE tunnels can be configured to transport traffic between two IPv4 networks or between two IPv6 networks.
- GRE tunnels can be used to connect an on-premises network to a cloud-based VPN. Cloud-based VPNs can provide a more secure and reliable connection than an on-premises VPN because they are not subject to the same physical security risks.
- GRE is often used in conjunction with IPsec to create a secure tunnel between two networks. IPsec encrypts the data inside the GRE tunnel to protect it from eavesdropping.
Drawbacks of GRE Generic Routing Encapsulation
GRE has a number of drawbacks:
- GRE is a proprietary protocol developed by Cisco. It is not an open standard like IPsec.
- GRE is not supported by all routers. In particular, many consumer-grade routers do not support GRE.
- GRE tunnels can be difficult to troubleshoot because they encapsulate the original packets and headers.
- GRE tunnels can introduce latency because the packets must be encapsulated and decapsulated at each end of the tunnel.
- GRE tunnels do not support multicast traffic.
- IPv4-only GRE tunnels cannot transport IPv6 traffic and vice versa. This can complicate the network configuration if both IPv4 and IPv6 traffic need to be transported.
- GRE tunnels can be susceptible to denial-of-service attacks.
How does generic routing encapsulation work?
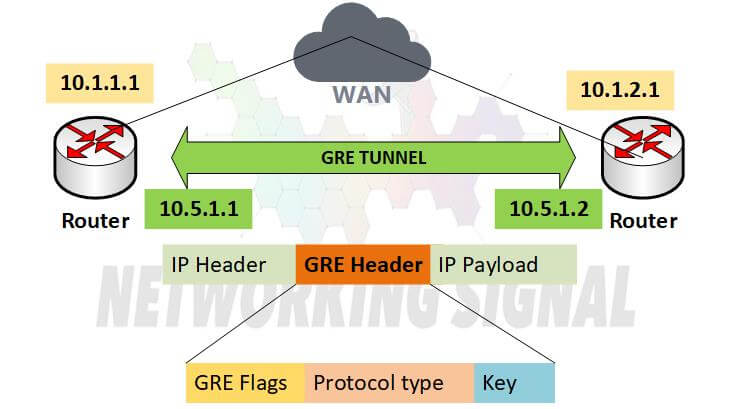
Here are the process steps for the GRE:
- A host on the private network sends a packet to a host on the public network.
- The router at the edge of the private network encapsulates the packet in a GRE header and forwards it to the router at the edge of the public network.
- The router at the edge of the public network decapsulates the packet and forwards it to the destination host on the public network.
- The destination host sends a reply packet to the source host.
- The router at the edge of the public network encapsulates the reply packet in a GRE header and forwards it to the router at the edge of the private network.
- The router at the edge of the private network decapsulates the packet and forwards it to the source host on the private network.
How to allow generic routing encapsulation?
If you want to allow GRE, you need to configure your router to allow GRE traffic. The specific steps will vary depending on the make and model of your router.
You can also use a software-based VPN solution that does not require GRE. Many VPN solutions, such as OpenVPN and IPsec, do not require GRE and can be used without any special router configuration.
is not configured to allow generic routing encapsulation?
If your router is not configured to allow GRE, you will need to reconfigure it.
Alternatives of GRE
If GRE is not supported by the routers in your network, or if you are looking for an alternative to GRE, consider using one of the following protocols:
IPsec is a standard protocol for creating VPNs. It can be used to create both site-to-site and remote-access VPNs.
OpenVPN is an open-source protocol that can be used to create both site-to-site and remote-access VPNs.
SSTP is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft. It can be used to create both site-to-site and remote-access VPNs.
L2TP is a legacy protocol that can be used in conjunction with IPsec to create a VPN. It is not as secure as IPsec alone, but it is more widely supported than IPsec.
PPTP is a legacy protocol that can be used to create both site-to-site and remote-access VPNs. It is not as secure as more modern protocols, but it is more widely supported than most modern protocols.

