What is Network Redundancy?
Network redundancy is a network design strategy used to provide an extra level of protection against network outages or other disruptions. It works by creating multiple routing paths through the network so that, if one path fails, others can take its place.
This ensures that even if one section of the network goes offline, data can still be routed from one end to the other, reducing downtime and improving reliability.
Example:
- A basic example of a redundant network includes two separate routers, each connected to different switches. This setup ensures that if one router fails, the other can take over, allowing data to continue flowing without interruption.
- In more complex situations, such as with large networks or multiple locations spread across geographically diverse areas, redundancy may involve using virtual local area networks (VLANs) or multiple Internet connections from different providers.
What are the Benefits of Network Redundancy?
Here are some of the key uses for network redundancy:
- Increased Network Uptime: By using redundant paths, it ensures that even if one section of the network fails, there are alternative routes that can take its place. This minimizes downtime and increases reliability and availability.
- Improved Fault Tolerance: Redundancy also helps to reduce the risk of a single point of failure. Having multiple routes ensures that even if one path fails, there is another backup route available.
- Increased Performance: Redundancy also helps to improve performance by allowing data traffic to be spread across multiple paths instead of overloading a single connection. This can result in faster data transfers and a better user experience.
- Cost Savings: Network redundancy can also help to reduce costs by eliminating the need for expensive backup systems or redundant hardware components. Having multiple paths ensures that even if one route fails, there is an alternative route available.
How Does Network Redundancy Work?
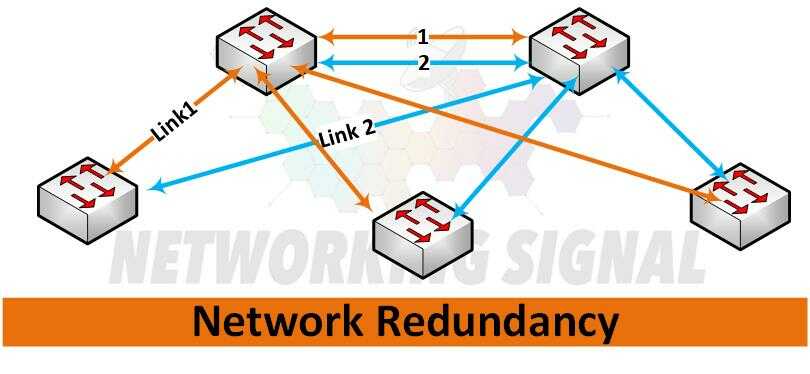
Here are the basic steps for implementing a redundant network:
1. Identify the Vulnerable Parts of Your Network:
You need to identify the parts of your network that are vulnerable to failure or disruption. This can range from single components such as routers and switches to entire sections such as data centers or long-distance connections.
2. Determine the Redundancy Requirements:
You need to determine how much redundancy is needed. This will depend on the criticality of the applications running on your network and how much downtime can be tolerated.
3. Create Different Paths for Data Traffic:
Once you’ve identified the vulnerable parts and determined your redundancy requirements, it’s time to create different paths for data traffic. This can involve using multiple routers, switches, Internet connections, VLANs, and other components.
4. Test the Redundant Network:
Finally, you need to test your redundant network to ensure that it’s working correctly and all the backup paths are functioning as expected. This involves testing each path individually as well as running simulations with multiple paths in use.


Very educative. Continue with the good work.