What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the Internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of buying, owning, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services, such as computing power, storage, and databases, on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider like Amazon Web Services (AWS).
With cloud computing, you no longer need to make large upfront investments in hardware and spend a lot of time on the heavy lifting of managing that hardware.
Instead, you can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need to power your newest bright idea or operate your IT department. You can access as much or as little as you need, almost instantly, and only pay for what you use.
What are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
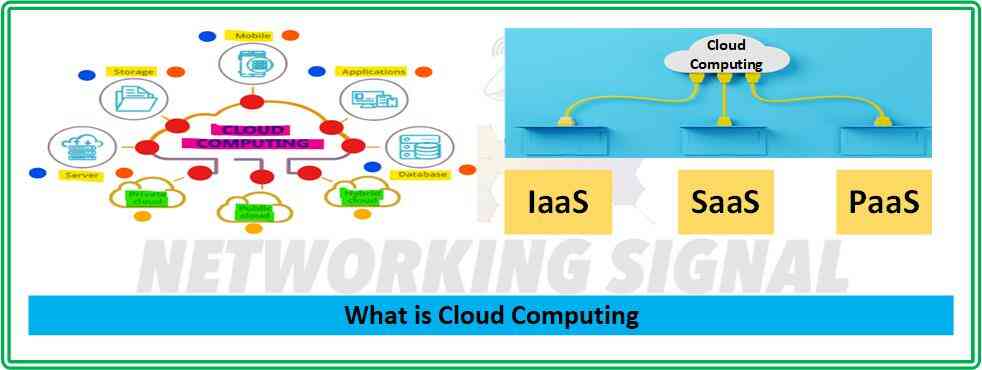
There are three types of cloud computing services:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
IaaS is the most basic and fundamental type of cloud computing service. It provides access to computing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking. With IaaS, you rent IT infrastructure from a cloud provider on an as-needed basis.
PaaS is a more complete offering than IaaS. It provides computing resources and additional services that make it easier to develop, run, and manage applications in the cloud. These services typically include development tools, a deployment environment, an application server, a middleware stack, and other tools for managing cloud-based applications.
SaaS is the most complete form of cloud computing service. It provides access to software applications that are hosted in the cloud and managed by the provider.
With SaaS, you don’t have to install or manage any software on your own computers, you just use the applications over the internet. Popular examples of SaaS include webmail, customer relationship management (CRM), and human resource management (HRM) applications.
What are the Characteristics of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, on-demand access to a shared pool of configurable resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
The five essential characteristics of cloud computing are:
On-demand self-service: A consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
Broad network access: Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, tablets, laptops, and workstations).
Resource pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand.
There is a sense of location independence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources but may be able to specify location at a higher level of abstraction (e.g., country, state, or data center).
Rapid elasticity: Capabilities can be rapidly and elastically provisioned, in some cases automatically, to quickly scale out and rapidly released to quickly scale in. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear unlimited and can be purchased in any quantity at any time.
Measured service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
How Cloud Computing Works?
The Working of Cloud Computing is divided into five layers.
- Client Layer: This layer consists of user devices such as computers, laptops, mobile phones, etc. that access cloud services over the internet.
- Data Layer: This layer stores data generated by various applications and services running on the cloud server. All the data stored in this layer is maintained by a separate team of data administrators.
- Application Layer: This layer consists of different software applications and services that are hosted on the cloud server. These applications can be accessed by users through the Internet.
- Cloud Server Layer: This layer handles all the server-related tasks such as hosting, networking, storage, etc. It is responsible for hosting the various applications and services running on the cloud.
- Cloud Management Layer: This layer provides all the necessary tools that are used to manage, monitor, and secure the cloud computing environment. It also includes authentication services, billing systems, etc.
These five layers work together to provide a complete cloud computing environment for users. The user devices connect to the cloud server and access the necessary applications, data, and services via the internet. The cloud management layer ensures that all the resources are managed efficiently and securely.
What are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
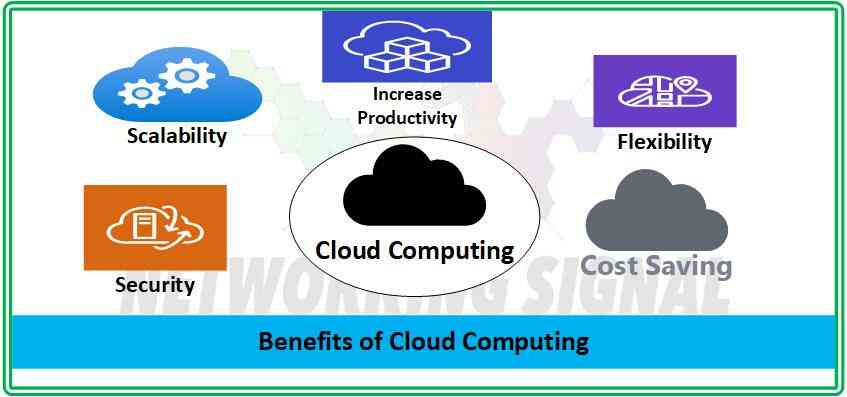
Cloud Computing offers numerous benefits over traditional computing environments. Some of the most prominent advantages include:
- Cost Savings: Cloud Computing reduces the need to invest in expensive hardware, software, and personnel for running an IT infrastructure. This can help businesses save a significant amount of money in terms of upfront costs and operational expenses.
- Increased Productivity: With cloud computing, businesses can access their data and applications from anywhere in the world. This allows for greater collaboration between departments and teams, resulting in increased productivity.
- Scalability: Cloud Computing allows businesses to quickly scale up or down depending on their changing needs. They can add or remove resources such as storage space and processing power without having to invest in new hardware.
- Flexibility: Cloud Computing gives businesses the flexibility to choose from a variety of applications and services, allowing them to customize their IT infrastructure according to their requirements.
- Security: Cloud Computing provides enhanced security compared to traditional computing environments. It allows for better data encryption, backup and disaster recovery solutions, and increased protection from cyber threats.
What are the Security Implications of Using the Cloud?
Although cloud computing offers numerous advantages, there are also some security implications that need to be considered when using the cloud.
- Data Theft: Cloud Computing can be vulnerable to cyber attacks such as data theft and malicious software. This means that sensitive information stored in the cloud may be at risk of being stolen or compromised.
- Unauthorized Access: Cloud Computing could also be vulnerable to unauthorized access. This means that if the cloud is not properly secured, malicious actors could gain access to the data and applications stored on the cloud server without permission.
- Data Loss: Cloud Computing can also be susceptible to data loss due to issues such as hardware failure or outages. This means that if the cloud server experiences any technical issues, the data stored on it could be lost.
See Also: Network Security Appliance: Benefits, Deploying Ways
Tips For Migrating Your Business to the Cloud
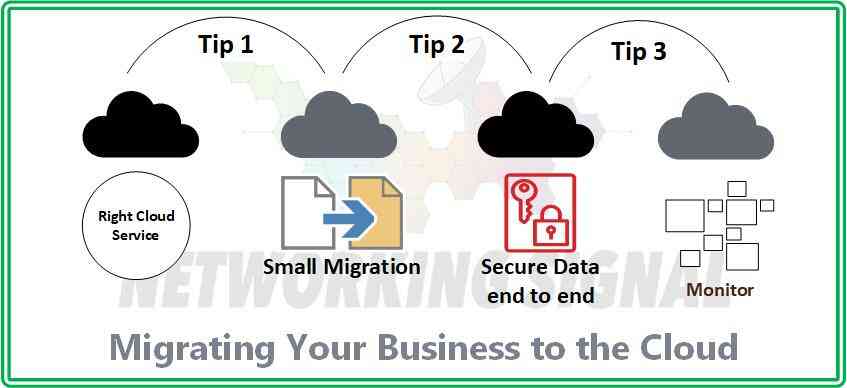
Migrating your business to the cloud can be a challenging process, but with the right strategies in place, it can be done successfully. Here are some tips for making the transition smooth and secure:
- Choose the Right Cloud Service Provider: It is important to choose a reliable cloud service provider that offers robust security features and reliable customer service. Research the different options available and select one that meets your needs and budget.
- Start with a Small Migration: It is best to start small when migrating to the cloud. Start by uploading only a few applications or files before moving on to bigger projects. This will ensure that you don’t overwhelm your system or experience any technical issues during the transition.
- Test Your System: Before fully committing to the cloud, it is important to thoroughly test your system and ensure that all security protocols are in place. This will help you identify any potential vulnerabilities or performance issues before they become a problem.
- Secure Data from End-to-End: It is essential to secure data from end-to-end, which means encrypting data in transit as well as at rest. This will ensure that your data remains safe and secure no matter where it is stored.
- Monitor Your System: Once you have successfully migrated to the cloud, it is important to regularly monitor your system for any performance or security issues. This will help ensure that your data and applications remain secure.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Provider for Your Business Needs?
Choosing the right cloud provider for your business needs is essential in ensuring a secure, successful migration to the cloud. Here are some tips for selecting the best provider for you:
- Research Different Providers: Research different providers to find one that meets your requirements and budget. Make sure to compare features such as pricing, security, scalability, and customer service.
- Assess Security Features: When selecting a cloud provider, make sure to assess their security features. Look for providers that offer robust encryption, authentication protocols, and disaster recovery services.
- Look For Flexible Solutions: Choose a provider that offers flexible solutions tailored to your business needs. This will ensure that you can scale up or down as needed and have the necessary resources to meet your changing requirements.
- Test before Implementing: Before fully committing to a cloud provider, make sure to thoroughly test their services to ensure that you’re getting what you need. This will help prevent any performance issues or security risks in the future.
What is the Future of Cloud Computing?
The future of Cloud Computing is bright, with the industry expected to grow exponentially in the coming years. The cloud will become increasingly important for businesses of all sizes as they rely on its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. As technology continues to develop, we can expect even more innovations in the field of cloud computing such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
Additionally, businesses will start relying more heavily on cloud storage for data backup and recovery. This will help ensure that their data remains secure and accessible in any emergency situation. All in all, the future of Cloud Computing is bright and has the potential to revolutionize the way businesses operate.