What is Local Area Network?
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a home, school, office building, or group of buildings. A LAN may be wired, wireless, or a combination of the two.
A typical LAN consists of cabling and one or more switches to connect the devices. Each node (computer, printer, etc.) on the network typically has its own network interface controller (NIC) through which it connects to the LAN.
A NIC is a piece of computer hardware that provides the appropriate mechanical, electrical, and communication interface between the computer and the network.
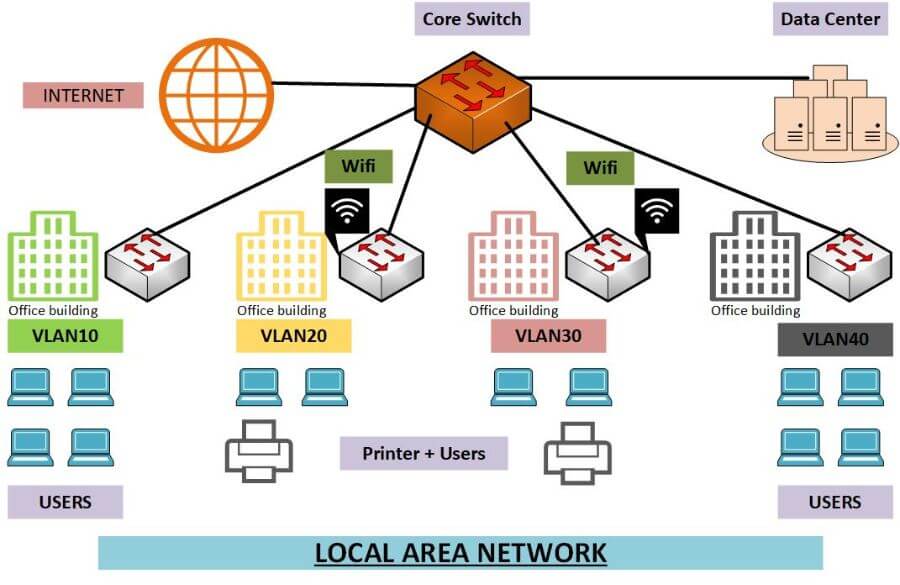
What are the Methods of Local Area Networks?
There are three common ways to build a Local Area Network. They include using:
- Ethernet
- Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi)
- Powerline networking
Ethernet is the most common method of connecting devices on a Local Area Network. It is fast, reliable, and relatively easy to set up. Ethernet uses a network cable to connect devices to a central device called a switch. The switch then connects to the router, which provides internet access.
Wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) is another common method of Local Area Networking. Wi-Fi uses radio waves to connect devices to the network without the need for wires or cables. Wi-Fi is convenient and easy to set up, but it is also more vulnerable to interference and security risks than wired Ethernet.
Powerline networking is a newer technology that uses the existing electrical wiring in your home or office to create a Local Area Network. Powerline adapters plug into an electrical outlet and use the power lines to connect devices to the network. Powerline networking is convenient and easy to set up, but it can be slower than other methods and is not always reliable.
What are the Advantages of Local Area Networks?
Here are some of the advantages of using a Local Area Network:
- LANs are fast and efficient, making them ideal for sharing resources such as files, printers, and internet connections.
- LANs are easy to set up and manage.
- LANs are more secure than Wide Area Networks (WANs) because they are not accessible to the general public.
- LANs are more reliable than WANs because they are not subject to the same kinds of disruptions.
What are the Disadvantages of Local Area Networks?
Here are some of the disadvantages of using a Local Area Network:
- LANs can be expensive to set up and maintain, especially if you need to use specialized equipment such as switches and routers.
- LANs can be difficult to troubleshoot if there are problems with the network.
- LANs can be vulnerable to security risks if they are not properly configured.
How does Media Access Work Via LAN?
There are two common methods of media access control on a Local Area Network:
- carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD)
- token passing
Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD) is the most common method of media access control. CSMA/CD allows all nodes on the network to listen to traffic before transmitting. If two nodes transmit at the same time, a collision occurs and both nodes must retransmit after a random amount of time.
Token passing is another method of media access control. Token passing allows only one node to transmit at a time. Nodes that want to transmit data must first wait for a token, which is a special data packet that allows them to transmit. When the node is finished transmitting, it passes the token to the next node in line. Token passing is more efficient than CSMA/CD, but it requires special hardware and is not commonly used.
How does Transmission Work Via LAN?
There are two common methods of data transmission on a Local Area Network:
- baseband
- broadband
Baseband is the most common method of data transmission. The baseband uses a single channel to transmit data. All nodes on the network share this channel, and only one node can transmit at a time.
Broadband is a newer method of data transmission. Broadband uses multiple channels to transmit data. This allows multiple nodes to transmit at the same time, which makes it more efficient than the baseband. However, broadband is more expensive and is not as commonly used as baseband.
Where Can We Use LANs?
Local Area Networks can be used in a variety of settings, including:
- homes
- small businesses
- large businesses
- schools
A home network is a Local Area Network that connects devices in your home, such as computers, printers, and game consoles. Home networks are convenient because they allow you to share resources and connect to the internet.
A small business network is a Local Area Network that connects devices in a small business, such as computers, printers, and servers. Small business networks are convenient because they allow you to share resources and connect to the internet.
A large business network is a Local Area Network that connects devices in a large business, such as computers, printers, and servers. Large business networks are convenient because they allow you to share resources and connect to the internet.
A school network is a Local Area Network that connects devices in a school, such as computers, printers, and servers. School networks are convenient because they allow you to share resources and connect to the internet.
Local Area Network Topologies
There are three common Local Area Network topologies:
- bus
- star
- mesh
Bus topology is the simplest and most common type of Local Area Network. In a bus topology, all nodes are connected to a single cable called a backbone. Bus topologies are easy to set up and manage, but they can be vulnerable to disruptions if the backbone is damaged.
Star topology is more complex than bus topology, but it is also more robust. In a star topology, all nodes are connected to a central device called a switch. The switch then connects to the router, which provides internet access. Star topologies are more expensive than bus topologies, but they are less vulnerable to disruptions.
Mesh topology is the most complex type of Local Area Network. In a mesh topology, each node is connected to every other node in the network. Mesh topologies are very robust and can be used in large or complex networks. However, they are also very expensive and can be difficult to set up and manage.
Local Area Network Protocols
There are two common Local Area Network protocols:
- Ethernet
- WiFi
Ethernet is the most common type of Local Area Network. Ethernet uses a special cable called a CAT5 or CAT6 cable to connect nodes to the network. Ethernet is fast and reliable, but it can be expensive to set up.
WiFi is a wireless Local Area Network protocol. WiFi uses radio waves to connect nodes to the network. WiFi is easy to set up but can be slower than Ethernet and is not always reliable.
Local Area Network Applications
Local Area Networks are used for a variety of applications including:
- file sharing
- printer sharing
- Internet access
File sharing is the most common application for Local Area Networks. File sharing allows users to share files between computers on the network. This can be useful for collaboration or for accessing files from multiple locations.
Printer sharing allows users to share printers between computers on the network. This can be useful for reducing the cost of printer hardware or for convenience.
Internet access is another common application for Local Area Networks. Internet access allows users to connect to the internet from multiple computers on the network. This can be useful for homes and small businesses that want to save money on internet access.
Local Area Network Security Risks
Local Area Networks are vulnerable to a variety of security risks including:
- malware
- viruses
- attacks from hackers
Malware is a type of software that can damage or disable computers. Malware can be spread through email attachments, infected websites, or infected files shared on the network.
Viruses are a type of malware that can replicate themselves and spread to other computers on the network. Viruses can be spread through email attachments, infected websites, or infected files shared on the network.
Hackers are individuals who attempt to gain unauthorized access to computer systems. Hackers can exploit security vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive data or disable systems.
Local Area Network Security Measures
Local Area Networks can be protected from security risks through the use of:
- firewalls
- antivirus software
- password protection
Firewalls are devices that can block or allow traffic between networks. Firewalls can be used to block traffic from malicious websites or stop attackers from gaining access to the network.
Antivirus software is a type of software that can detect and remove viruses from computers. Antivirus software is typically installed on all computers on a Local Area Network.
Password protection is a type of security measure that requires users to enter a password to access data or resources. Password protection can restrict access to sensitive data or prevent unauthorized changes to system settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is LAN architecture secure?
Yes, LAN architecture is quite secure. It has the capability to protect the data exchanged between computers on the same network by using various encryption protocols and authentication methods.
What is the main purpose of LAN?
The main purpose of LAN is to enable computers or other devices to communicate and share resources, such as files, printers, and applications. Through a local area network (LAN), users can access a shared file system and send messages or information to one another.
How many nodes are in a LAN?
The number of nodes in a LAN can vary depending on the type and size of the network. Generally, LANs are made up of fewer than 10 computers but can include more as needed.
Can a single computer by a LAN?
Yes, a single computer can be a LAN. This type of network is referred to as a peer-to-peer network and is commonly used in home networks or small office environments.
Is a LAN Faster than an Internet?
Yes, a LAN is usually faster than the internet due to its small size and lack of interference from other networks. With fewer users on the network, data can be transferred more quickly between computers on the same local area network.

