A MAC address is a unique identifier for a network adapter. MAC addresses are used in the media access control protocol sublayer of the data link layer of a network. A MAC address can be used to identify the manufacturer of a network card or other networking device. MAC addresses are sometimes referred to as hardware addresses or physical addresses.
MAC addresses are 6 bytes long and are typically represented in hexadecimal notation. MAC addresses are typically assigned by the manufacturer of a network card or other networking device. A MAC address can be manually configured on a network device, but this is not typically done.
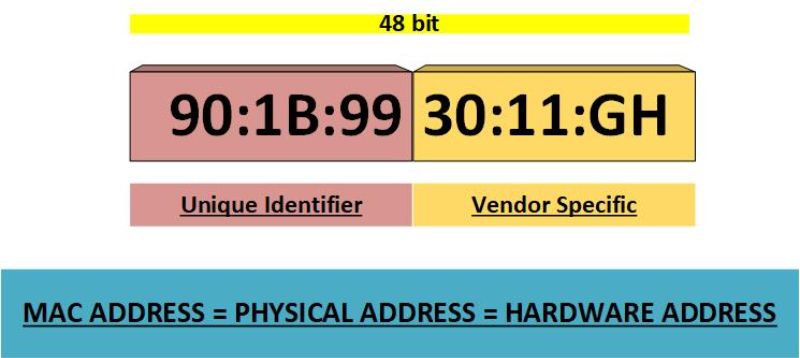
The first 3 bytes of a MAC address are the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI). The OUI is used to identify the manufacturer of the network card or other networking device. The remaining 3 bytes of the MAC address are typically assigned by the manufacturer in a way that ensures that each MAC address is unique.
How does MAC Address work on Data Link Layer?
Here are the steps that occur when a network device sends data on a network:
1. The network device creates a data frame, which includes the data to be sent and the MAC address of the destination device.
2. The network device checks the MAC address of the destination device against a list of MAC addresses that it has stored. This list is known as the Media Access Control (MAC) address table.
3. If the MAC address of the destination device is in the MAC address table, the network device sends the data frame to the destination device.
4. If the MAC address of the destination device is not in the MAC address table, the network device broadcasts the data frame to all devices on the network.
Look Here:
What are the Basic Issues of MAC Addresses and How To Troubleshoot Them?
MAC Address into Frame
When a network device sends data on a network, it creates a data frame. The data frame includes the data to be sent and the MAC address of the destination device. The MAC address is used by the devices on the network to identify the source and destination of the data.
Look Here:
Size of MAC Address in Frame
The MAC address is 6 bytes long and is typically represented in hexadecimal notation. The MAC address is used by the devices on the network to identify the source and destination of the data.
Location of MAC Address in Frame
The MAC address is typically located in the header of the data frame. The title is the first part of the data frame that is sent on the network. The MAC address is used by the devices on the network to identify the source and destination of the data.
What is MAC Address Table?
A MAC address table is a data structure used by network devices to store the MAC addresses of other devices on the network. The MAC address table is used by the device to determine where to forward packets. MAC address tables are typically stored in memory and are sometimes referred to as CAM tables.
When a packet is received by a network device, the device looks up the destination MAC address in its MAC address table. The packet is forwarded to the next hop if the MAC address is found. If the MAC address is not found, the packet is typically discarded.
MAC address tables can become full if too many devices are connected to the network. When this happens, the network device may start to behave erratically or may even stop working altogether.
Look Here:
Aging Time of MAC Address Table
The aging time of a MAC address table is the amount of time that a MAC address can remain in the table without being used. The purpose of the aging time is to prevent the MAC address table from becoming full. When the aging time expires, the MAC address is removed from the table.
The aging time of a MAC address table can be configured on a network device. The default aging time is typically 10 minutes.


1 thought on “What is a MAC Address and How Does Work in Data Link Layer?”