It is a Link State Protocol which protocol working on links call link-state protocol & Router adds link information to the Database. In Distance Vector Protocol we know about only neighbours but in Link State behaviour everyone makes their own database and shares it with all Routers. OSPF states of the open shortest path first with a basic guide are below.
For example, if we have Six Router then six databases will be shared with each other and through this database, we can create a topology or tree for the same.
OSPF is a layer three protocol with 89 numbers. It is a classless protocol.
It is uses multicast address 224.0.0.5 & 224.0.0.6.
OSPF uses the concept of AREAs do not compare it with AS with basic of EIGRP (Autonomous System), basically, both are designed for different uses. EIGRP for enterprise and OSPF for the internet or wide area
Note* An interface is a member of an AREA, not a Router.
In a Router for enabling OSPF, we are using Command: #Router OSPF < process ID>

A router first elects a Router ID. There are three ways to elect a Router ID
- Manually we can set
- Highest Loopback interface address
- Highest Physical interface address
Note* Router ID is used to represent a router in a Domain.

By this Enable OSPF on Routers:
- Start sending hello for dynamic discovery.
- Add links to its Database in neighbouring state
The OSPF States are:
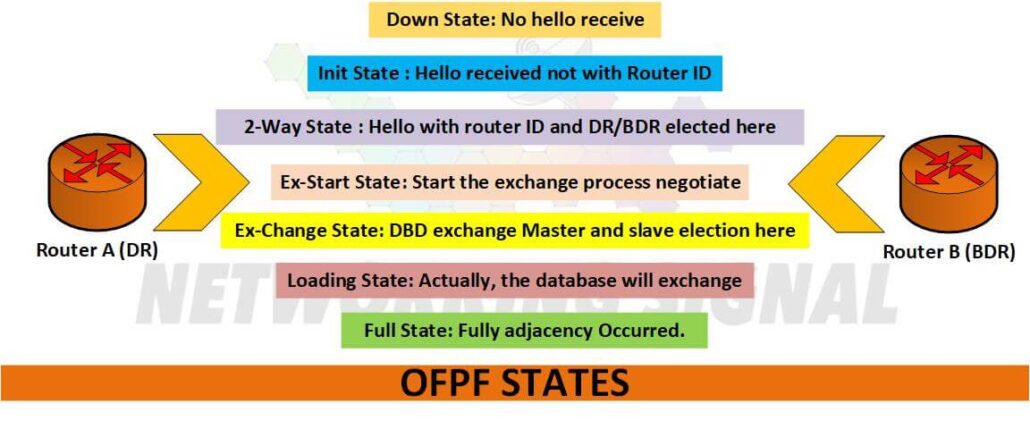
Down>In-it>2Way>Ex-start>Ex-change>Loading>Full
Down State:

No hello has been received from a neighbour as the interface is down.
Active neighbour Field: Add R2 router ID if R2 exists neighbour. The new neighbouring R1 does not know the R2 router ID.
For example: if I call my friend I will call him by his name and if I call a stranger then I call with a hello and tell me your name, I want to friendship with you.
Init State:
Hello received it but not with the router ID.
2-Way State:

After that hello send then Active field with R2 router ID this state is a 2-way state. (DR BDR election in this state and we will discuss this topic in the next blog). Establish 2-way communication now routers know about each other.
Hello packet Parameter:
Ex-start State:
Start the exchange process negotiate – MTU and Sequence number (For Reliability).
Ex-Change State:
DBD exchange (Database Descriptors) Master and slave election here for exchange DBD
R1 sends its own DBD with the sequence number, which router ID is the highest sequence number used for exchange DBD.
Loading State:
Actually, the database will exchange in this state.
Full State:
Fully adjacency Occurred.
Here these are commands
- #Show IP OSPF: use for show OSPF configuration.
- #Show IP OSPF interface: show the interface detail which is enabled with OSPF.
- #Show IP OSPF Neighbor: Detail of neighbours
- #Show IP OSPF Database: Detail of all router network links within the Area.
This is all about Basic OSPF with P2P or serial link and how it configures on the router. This will help you with OSPF knowledge and in the next OSPF blog, I will discuss BR DBR and the area’s role in a broadcast network.


1 thought on “OSPF States of Open Shortest Path First with Basic Guide”