Public IP Address
A public IP address is an IP address that can be accessed over the Internet. Public IP addresses are used in order to allow devices to connect to each other and communicate over the internet. A public IP address is assigned to a device by an Internet service provider (ISP).
Uses of Public IP Address
There are a number of uses for public IP addresses, some of which are listed below:
To connect to the internet: In order to connect to the internet, devices need to have a public IP address. This is because when you connect to the internet, your device will be communicating with other devices all over the world.
To host a website: In order to host a website, you will need to have a public IP address. This is because when someone visits your website, they will be connecting to your device from the internet.
To send and receive email: When you send or receive an email, your device will be communicating with email servers that have public IP addresses.
To use online services: There are many online services that require you to have a public IP address in order to use them. Examples of such services include online gaming, VoIP (Voice over IP), and remote desktop access.
Range of Public IP Address
Public IP addresses are assigned to devices by ISPs. The range of public IP addresses is defined by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). ICANN has reserved the following three blocks of IP addresses for public use:
• Class A: 1.0.0.0 to 9.0.0.0, 11.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255
• Class B: 128.0.0.0 to 172.15.0.0, 172.32.0.0 to 191.255.255.255
• Class C: 192.0.0.0 to 192.167.0.0, 192.169.0.0 to 223.255.255.255
Private IP Address
A private IP address is an IP address that is not intended to be used outside of a private network. A private IP address is assigned to a device within a private network and is typically not accessible over the Internet. Private IP addresses are usually used in order to keep devices within a private network hidden from the public.
Uses of Private IP Address
There are a number of uses for private IP addresses, some of which are listed below:
To keep devices within a private network hidden: By using private IP addresses, devices within a private network can be kept hidden from the public. This is because private IP addresses are not intended to be used outside of the network.
To improve security: Private IP addresses can be used to improve security because they make it more difficult for attackers to find and target devices within a network.
To reduce the number of public IP addresses: By using private IP addresses, the number of public IP addresses that are required can be reduced. This is because private IP addresses can be reused within different private networks.
Range of Private IP Address
Private IP addresses are typically assigned to devices within a private network. The range of private IP addresses is defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). IETF has reserved the following three blocks of IP addresses for private use:
• Class A: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
• Class B: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
• Class C: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Private IP Address vs Public IP Address: Key Differences
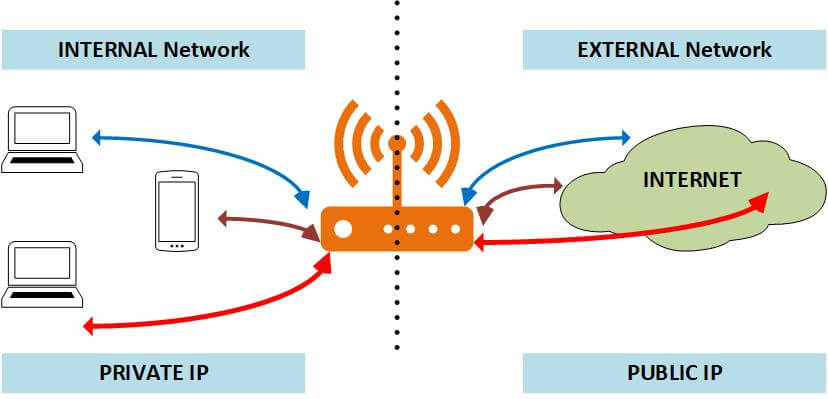
There are a number of differences between public and private IP addresses, some of which are listed below:
| Public IP Address | Private IP Address | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Public IP addresses are assigned to devices by an ISP | Private IP addresses are typically assigned to devices within a private network |
| 2 | Public IP addresses can be used to connect to the internet | Private IP addresses are usually used in order to keep devices within a private network hidden from the public. |
| 3 | The range of public IP addresses is defined by ICANN | The range of private IP addresses is defined by IETF |
| 4 | Public IP addresses are globally unique | private IP addresses can be reused within different private networks |
| 5 | Public IP addresses are typically used for devices that need to be accessible over the internet | Private IP addresses are usually used for devices that do not need to be accessible over the internet. |
| 6 | Range: Class A: 1.0.0.0 to 9.0.0.0, 11.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255 Class B: 128.0.0.0 to 172.15.0.0, 172.32.0.0 to 191.255.255.255 Class C: 192.0.0.0 to 192.167.0.0, 192.169.0.0 to 223.255.255.255 | Range: Class A: 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255 Class B: 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255 Class C: 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255 |

