What is SDWAN?
SDWAN is a software-defined networking technology that allows for the creation of virtualized network overlays. SDWAN provides a number of benefits over traditional networking approaches, including improved flexibility, scalability, and performance.
SDWAN is typically implemented as an overlay network, which means that it sits on top of an existing physical network infrastructure. This allows SDWAN to be deployed without the need to replace existing networking equipment.
What are the Benefits of SDWAN?
Improved Flexibility: The biggest advantage of SDWAN is its improved flexibility. Unlike traditional networking approaches, SDWAN allows for the creation of virtualized network overlays. This means that networks can be quickly and easily provisioned and reconfigured to meet changing needs.
Improved Scalability: A key benefit of SDWAN is its improved scalability. SDWAN allows for the creation of multiple virtualized network overlays, each of which can be independently scaled to meet the needs of a particular application or workload. This makes it easy to scale networks up or down as needed, without having to make major changes to the underlying infrastructure.
Improved Performance: A key benefit of SDWAN is its improved performance. By creating a virtualized network overlay, SDWAN can reduce the amount of traffic that needs to be sent over the underlying physical infrastructure. This can lead to significant improvements in network performance and reliability.
Enhanced Security: Another key benefit of SDWAN is its enhanced security. By creating a virtualized network overlay, SDWAN can isolate traffic and protect sensitive data from being exposed to the public internet. In addition, SDWAN can encrypt traffic to further protect data.
Reduced Complexity: SDWAN can also help to reduce the complexity of networks. By abstracting away the underlying physical infrastructure, SDWAN can make it easier to deploy and manage complex network environments.
Increased Agility: The increased flexibility of SDWAN also allows for increased agility. Networks can be quickly and easily provisioned and reconfigured to meet changing needs. This can help organizations rapidly respond to new opportunities and threats.
Better Quality of Service (QoS): SDWAN can also provide a better quality of service (QoS). By creating a virtualized network overlay, SDWAN can ensure that critical applications and services receive the resources they need. This can help to improve application performance and reduce downtime.
Greater Efficiency: SDWAN can also lead to greater efficiency. By creating a virtualized network overlay, SDWAN can reduce the amount of traffic that needs to be sent over the underlying physical infrastructure. This can help to improve network utilization and reduce costs.
Lower Costs: One of the biggest benefits of SDWAN is its potential to lower costs. By using a software-defined approach, SDWAN can reduce the need for expensive proprietary hardware. In addition, SDWAN can help to reduce the complexity of networks, which can lead to further cost savings.
Seamless Integration: SDWAN can also be easily integrated into existing network environments. By using a standard IP-based approach, SDWAN can be deployed without the need to replace existing networking equipment. This allows for a seamless transition to SD-WAN without disrupting current operations.
Multi-Site Connectivity: Another key benefit of SD-WAN is its ability to connect multiple sites. SDWAN can be used to create a single, unified network that spans multiple locations. This can help to improve communication and collaboration between employees.
WAN Optimization: SDWAN can also help to optimize WAN performance. By creating a virtualized network overlay, SDWAN can reduce the amount of traffic that needs to be sent over the underlying physical infrastructure. This can lead to significant improvements in WAN performance and reliability.
Application-Aware Routing: SDWAN can also provide application-aware routing. By using a software-defined approach, SDWAN can intelligently route traffic based on application needs. This can help to improve application performance and reduce network congestion.
Increased Visibility and Control: SDWAN can also provide increased visibility and control over network traffic. By using a software-defined approach, SDWAN can give administrators granular control over how traffic is routed and prioritized. This can help to ensure that critical applications and services receive the resources they need.
What are the Drawbacks of SDWAN?
Here are some potential drawbacks of SDWAN:
Increased Complexity: One potential drawback of SDWAN is its increased complexity. By using a software-defined approach, SDWAN can make it more difficult to troubleshoot and manage network environments. This can lead to increased costs and decreased productivity.
Lack of Standardization: Another potential drawback of SDWAN is its lack of standardization. Because SD-WAN is still a relatively new technology, there is no clear industry standard for how it should be deployed and managed. This can make it difficult for organizations to compare and contrast different SD-WAN solutions.
Security Concerns: Another potential concern with SDWAN is its security. Because SDWAN creates a virtualized network overlay, it can create new security risks. This is because the overlay network is not subject to the same physical security controls as the underlying physical infrastructure.
What are the Components of SDWAN?
There are four main components of SDWAN:
- network overlay
- controller
- edge devices
- orchestrator
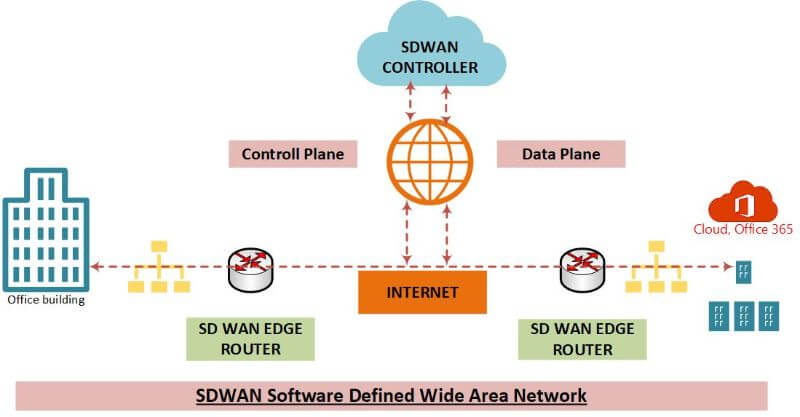
Network Overlay: The network overlay is the virtualized network that is created by SDWAN. This overlay network sits on top of the underlying physical infrastructure and provides a logical view of the network.
SD-WAN Controller: The controller is the central point of control for SD-WAN. The controller is responsible for managing and configuring the network overlay. In addition, the controller can be used to provide visibility into network traffic and monitor performance.
The Edge Devices: Edge devices are devices that are located at the edge of the network. Edge devices are responsible for forwarding traffic to and from the network overlay. In addition, edge devices can be used to provide visibility into network traffic and monitor performance.
SD-WAN Solutions
There are many different solutions that can be used to implement SDWAN. Here are a few of the most popular:
- Cisco SDWAN
- VMware NSX SDWAN
- Versa Networks SDWAN
- Silver Peak SDWAN
- Fortinet SDWAN
- PaloAlto SDWAN
Cisco SDWAN, VMware NSX SDWAN, Versa Networks SDWAN, Silver Peak SDWAN, Fortinet SDWAN, and Palo Alto SDWAN are popular solutions for implementing SDWAN. SDWAN uses an application-aware approach to routing traffic. This helps to ensure that critical applications and services receive the resources they need. In addition, SDWAN provides increased visibility and control over network traffic.
What are the Parameters of SDWAN?
There are many different parameters that can be used to configure SDWAN. Here are a few of the most common:
- Bandwidth
- Latency
- Jitter
- Packet loss
Bandwidth, latency, jitter, and packet loss are all important parameters for configuring SDWAN. By carefully configuring these parameters, organizations can ensure that their SDWAN solution meets their specific needs.
How to Deploy SDWAN?
There are many different ways to deploy SDWAN. Here are a few of the most common:
- On-premises
- Cloud-based
- Hybrid
On-premises: On-premises SDWAN deployment is when the SDWAN solution is deployed on the organization’s premises. This can be done either by using physical hardware or by using a virtual appliance.
Cloud-based: Cloud-based SDWAN deployment is when the SDWAN solution is deployed in the cloud. This can be done either by using a cloud-based controller or by using a hybrid deployment model.
Hybrid: Hybrid SDWAN deployment is when the SDWAN solution is deployed both on-premises and in the cloud. This allows organizations to get the best of both worlds by leveraging the benefits of both on-premises and cloud-based deployments.
What is the Future of SDWAN?
The future of SDWAN is very exciting. As more and more organizations adopt SDWAN, we can expect to see continued innovation in this area. In addition, we can expect to see more companies offering SDWAN solutions and more organizations deploying SDWAN.
SDWAN is the future of networking. It provides a number of benefits over traditional networking solutions. In addition, SDWAN is very flexible and can be deployed in a number of different ways.
Does SDWAN Replace MPLS?
MPLS is a traditional networking solution that has been around for many years. MPLS is a very reliable solution, but it has a number of limitations. SDWAN is a newer solution that offers a number of advantages over MPLS. As such, SDWAN is often seen as a replacement for MPLS.
Can We use SDWAN For Home Network?
Yes, SDWAN can be used for home networking. Home networking is a great use case for SDWAN because it can provide increased flexibility and control over the network. In addition, SDWAN can help to improve network performance.
What is the Relationship Between SDWAN and WAN?
WAN is a network that connects two or more LANs. SDWAN is a solution that can be used to improve the performance of a WAN. SDWAN does this by using an application-aware approach to routing traffic. This helps to ensure that critical applications and services receive the resources they need. In addition, SDWAN provides increased visibility and control over network traffic.

