What are SNAT and DNAT?
SNAT and DNAT are both types of network address translation (NAT). NAT is a method used to remap one IP address space into another. This allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single public IP address.
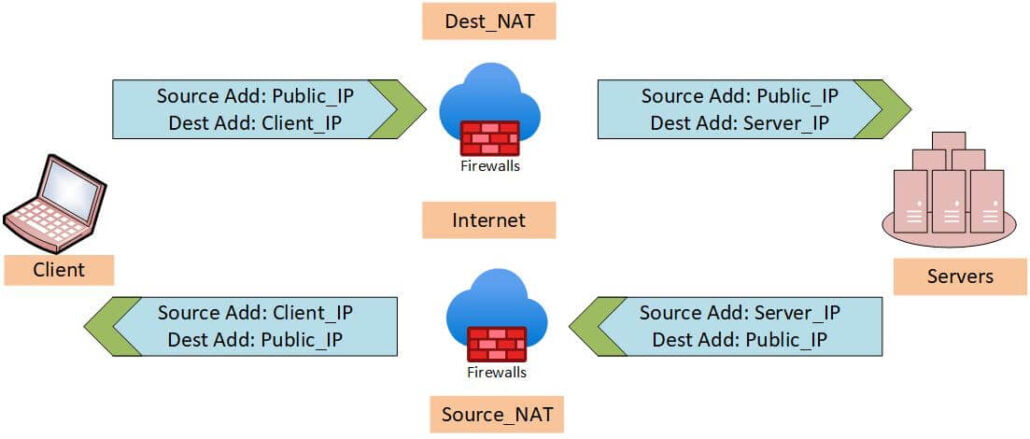
SNAT is used when packets originate from a private network and need to be sent to a public network. The source IP address is changed to a public IP address before the packet is sent.
- Example of Source NAT: A user on a private network wants to access a website on the public Internet.
DNAT is used when packets originate from a public network and need to be sent to a private network. The destination IP address is changed to a private IP address before the packet is sent.
- Example of Destination NAT: A user on the public Internet wants to access a website hosted on a private network.
Both Source NAT and Destination NAT can be used to allow communication between a private network and a public network. NAT can also be used to improve security by hiding the internal structure of a network from outsiders.
SNAT vs DNAT: Key Differences
Here are the key differences on basis of different parameters between SNAT and DNAT:
| Source NAT (SNAT) | Destination NAT (DNAT) | |
|---|---|---|
| SNAT is used when the packets originate from a private network and are sent to a public network | DNAT is used when the packets originate from a public network and are sent to a private network | |
| In SNAT, the source IP address is changed to a public IP address before sending it | In DNAT the destination IP address is changed to a private IP address | |
| SNAT is used to allow communication from the private network to the public network | DNAT is used to allow communication from the public network to the private network | |
| The main purpose of SNAT is to preserve the source IP address of the packets | The main purpose of DNAT is to change the destination IP address | |
| SNAT is performed by the network devices located in the private network | DNAT is performed by the network devices located in the public network | |
| Due to SNAT, the return traffic from public to private can be routed properly | In DNAT, the return traffic is routed to the original destination without any translation |
How does IP Address Translate with the Help of SNAT and DNAT?
Network address translation (NAT) is the process of translating an IP address from one form to another. NAT is used to map a group of private IP addresses to a single public IP address. This allows multiple devices on a local network to share a single Internet connection.
How do DNAT and SNAT work on the Router?
DNAT and SNAT are performed by the router. The router is responsible for forwarding packets between networks.
Here are the steps that the router takes to perform DNAT:
1. The router receives a packet from the public network.
2. The router looks up the destination IP address in its NAT table.
3. The router finds the private IP address that is associated with the public IP address.
4. The router changes the destination IP address to the private IP address.
5. The router forwards the packet to the private network.
Here are the steps that the router takes to perform SNAT:
1. The router receives a packet from the private network.
2. The router looks up the source IP address in its NAT table.
3. The router finds the public IP address that is associated with the private IP address.
4. The router changes the source IP address to the public IP address.
5. The router forwards the packet to the public network.