What is Firewall in Networking?
A firewall is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing network traffic and controls access to your network. Firewalls are often categorized as either network firewalls or host-based firewalls.
Network firewalls filter traffic between multiple devices on a network, while host-based firewalls provide a layer of software security on individual devices.
Firewalls can be hardware appliances, software programs, or a combination of both. Hardware firewalls are typically installed on a network router and protect an entire network.
Software firewalls are installed on individual devices and only protect that one device. Some routers have built-in firewall features that can be enabled to provide basic protection for a home network.
What are the Types of Firewalls?
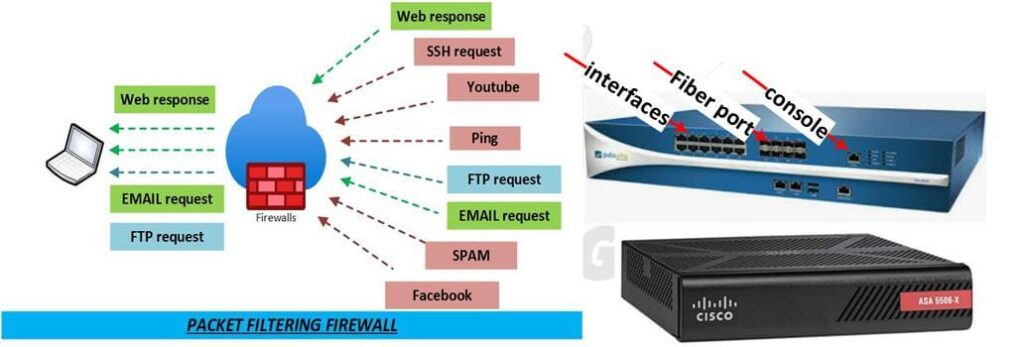
There are several different types of firewalls that are used to protect networks and devices. The most common types of firewalls include:
Packet filtering firewall: This type of firewall inspects each packet that comes into a network and checks the header information to see if it is allowed to enter. Packet filtering firewalls can be configured to allow or block traffic based on various criteria, such as the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols.
Stateful inspection firewall: Also known as a dynamic packet filtering firewall, this type of firewall keeps track of the state of each connection passing through it. Stateful inspection firewalls can inspect packets in context and make decisions about whether to allow or block them based on the state of the connection.
Application-level firewall: This type of firewall inspects traffic at the application layer, which is the highest level of the OSI model. Application-level firewalls are also known as proxy servers because they act as intermediaries between clients and servers. Proxy servers can be configured to allow or block traffic based on the content of the traffic, such as specific websites or applications.
What are the Components of a Firewall?
A firewall typically consists of the following components:
- Filter Engine: The filter engine is the heart of the firewall and is responsible for inspecting traffic and deciding whether to allow or block it.
- Policy Engine: The policy engine is responsible for enforcing the rules that have been configured in the firewall. The policy engine determines which traffic should be allowed or blocked based on the filter rules.
- CPU: The CPU is responsible for processing the data that passes through the firewall.
- Memory: The memory stores the data that is being processed by the CPU.
- Management Interface: The management interface is used to configure the firewall and view statistics about the traffic that has been passing through it. The management interface can be a web-based interface, a command-line interface, or a graphical user interface.
- WAN Interface: The WAN interface is used to connect the firewall to the internet.
- LAN Interface: The LAN interface is used to connect the firewall to the local network.
- Console Interface: The console interface is used to connect the firewall to a local computer for administration purposes.
What are the Benefits of a Firewall?
Firewalls provide a number of benefits for both home and business networks Some of the benefits of using a firewall include:
- Security: Firewalls help to protect your network from external threats such as hackers and malware.
- Privacy: Walls can also help to protect the privacy of your network by blocking unwanted traffic such as advertising or spyware.
- Performance: Firewalls can improve the performance of your network by blocking unwanted traffic and reducing the amount of data that is transferred through the network.
- Reliability: Firewalls can help to make your network more reliable by blocking traffic that could cause problems such as denial-of-service attacks.
What are the Drawbacks of a Firewall?
There are a few drawbacks to using firewalls, such as:
- Complexity: Firewalls can be complex to configure and manage.
- Incompatibility: Some types of firewalls can be incompatible with certain types of equipment or software.
- Restrictions: Firewalls can restrict the use of certain features of your network, such as file sharing or remote access.
- Overclocking: Firewalls can sometimes block legitimate traffic, such as email or website traffic.

