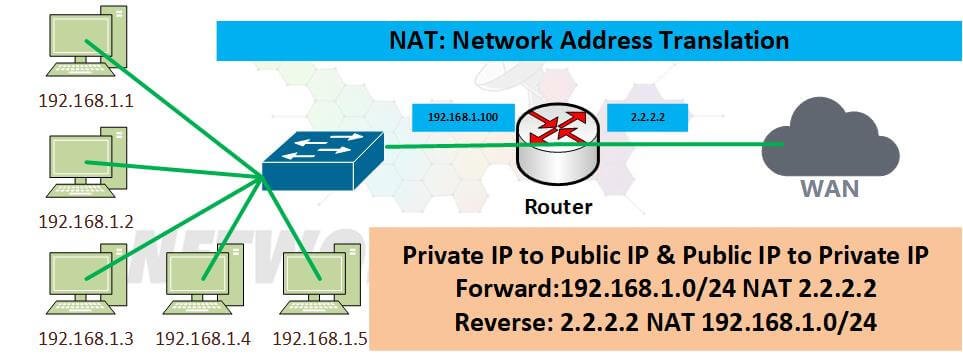
NAT is a network address translation technology that is used to map private IP addresses to public IP addresses. This allows businesses and individuals to use private IP addresses for their internal networks while still being able to connect to the Internet. NAT can also be used to provide Internet access for devices that do not have a public IP address, such as printers and scanners.
Types of NAT
There are three main types of NAT: static NAT, dynamic NAT, and PAT.
Static NAT: Static NAT mapping is a one-to-one mapping between a private IP address and a public IP address. This type of NAT is typically used when you need to allow incoming traffic from the Internet to reach a specific device on your network, such as a Web server.
Dynamic NAT: Dynamic NAT mapping is a one-to-one mapping between a private IP address and a public IP address that is chosen from a pool of available public IP addresses. This type of NAT is typically used when you need to allow outgoing traffic from your internal network to reach the Internet.
PAT: A PAT mapping is a many-to-one mapping between a private IP address and a public IP address. This type of NAT is typically used when you need to allow outgoing traffic from multiple devices on your internal network to reach the Internet using a single public IP address.
See Also: Public IP vs Private IP Address: 6 Key Differences
Uses of NAT
There are several reasons why you might want to use NAT:
- To allow devices on your internal network to connect to the Internet without giving them each a public IP address.
- To conserve public IP addresses.
- To hide the true addresses of devices on your internal network from the outside world.
- To provide additional security for your internal network by hiding the addresses of your devices from potential attackers.
- To allow you to use private IP addresses on your internal network while still being able to connect to the Internet.
NAT can be used in conjunction with other technologies, such as a firewall, to provide additional security for your network.
Differentiate NAT vs PAT
PAT is a specific form of NAT that uses a single public IP address to map multiple private IP addresses. NAT can be used in a similar way, but it can also be used to provide Internet access for devices that do not have a public IP address, such as printers and scanners.
PAT is typically used when you need to allow outgoing traffic from multiple devices on your internal network to reach the Internet using a single public IP address. NAT can also be used to provide security for your network by hiding the addresses of your devices from potential attackers.
Importance of NAT
NAT is an important technology for businesses and individuals that use private IP addresses for their internal networks. NAT can help to conserve public IP addresses, hide the true addresses of devices on your internal network, and provide additional security for your network.

