What is OSI Model?
The OSI Model is a seven-layer model that defines the different components of a network system and how they interact with each other. The OSI Model is a reference model that was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984.
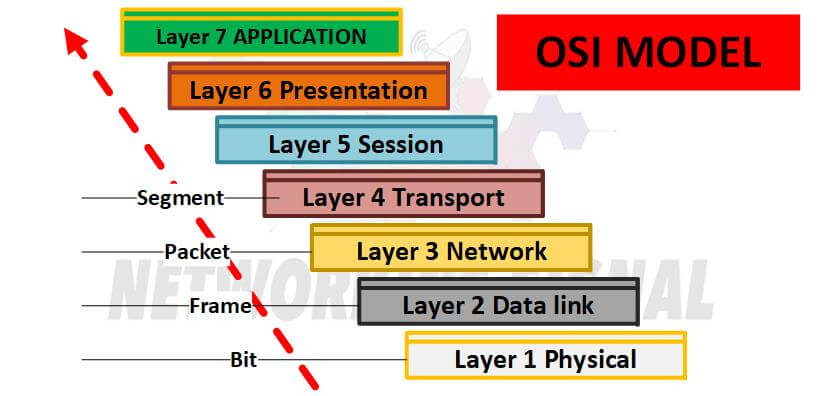
What are the 7 Layers of the OSI Model?
The OSI Model is divided into seven layers, each of which represents a different aspect of networking:
Layer 1: Physical Layer
The Physical Layer is the first layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for transmitting raw data over a physical medium, such as a copper cable or optical fiber. The Physical Layer defines the electrical, mechanical, and procedural characteristics of the interface between a network and the devices that connect to it.
Layer 2: Data Link Layer
The Data Link Layer is the second layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for the error-free transmission of data over a physical medium. The Data Link Layer defines the logical relationships between nodes, such as how data is packaged into frames and how frames are routed from one node to another.
Layer 3: Network Layer
The Network Layer is the third layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for routing data between nodes. The Network Layer defines the logical relationships between network devices, such as how data is routed through a network.
Layer 4: Transport Layer
The Transport Layer is the fourth layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for end-to-end error-free delivery of data. The Transport Layer defines the mechanisms that are used to ensure that data is delivered reliably and in sequence.
Layer 5: Session Layer
The Session Layer is the fifth layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for establishing, maintaining, and terminating sessions between nodes. The Session Layer defines the procedures that are used to establish, maintain, and terminate communication between nodes.
Layer 6: Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer is the sixth layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for translating data between different formats. The Presentation Layer defines the procedures that are used to translate data between different formats.
Layer 7: Application Layer
The Application Layer is the seventh layer of the OSI Model and is responsible for providing services to application programs. The Application Layer defines the procedures that are used to provide services to application programs.
What are the Examples of the OSI Model?
There are several examples of the OSI Model:
- Ethernet is a Layer 2 technology that is used to connect computers in a LAN.
- IPv4 is a Layer 3 protocol that is used to route data across networks.
- TCP is a Layer 4 protocol that is used to ensure the reliable delivery of data.
- HTTP is a Layer 7 protocol that is used to exchange data between web browsers and web servers.
What are the Advantages of the OSI Model?
There are several advantages of the OSI Model:
- The OSI Model is a standard that is used by vendors to develop products that are compatible with each other.
- The OSI Model is a reference model that can be used to compare different networking architectures.
- The OSI Model can be used to develop new networking technologies.
- The OSI Model can be used to troubleshoot networking problems.
What are the Disadvantages of the OSI Model?
There are several disadvantages of the OSI Model:
- The OSI Model is a complex model that can be difficult to understand.
- The OSI Model is not a protocol, and it does not define how data should be formatted or transmitted.
- The OSI Model is not widely used in practice, and many networking technologies do not follow the model.
- The OSI Model is not a perfect model, and it has some limitations.
What is the Relation between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model?
The TCP/IP Model is a simplified version of the OSI Model, and it is the most widely used model for networking. The TCP/IP Model has four layers: the Application Layer, the Transport Layer, the Internet Layer, and the Link Layer. The TCP/IP Model is a more practical model than the OSI Model, and it is the model that is used by the Internet.
See Also: OSI model vs TCP/IP Model ( Comparison )
How to Remember the OSI Model?
Here are the easy mnemonics to remember the OSI Model:
Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away (Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application)
All People Seem To Need Data Processing (Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical)
Annie’s Pet Sells Dogs Properly (Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical)
A Poor Singer Takes Heedless Risks Performing (Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical)

