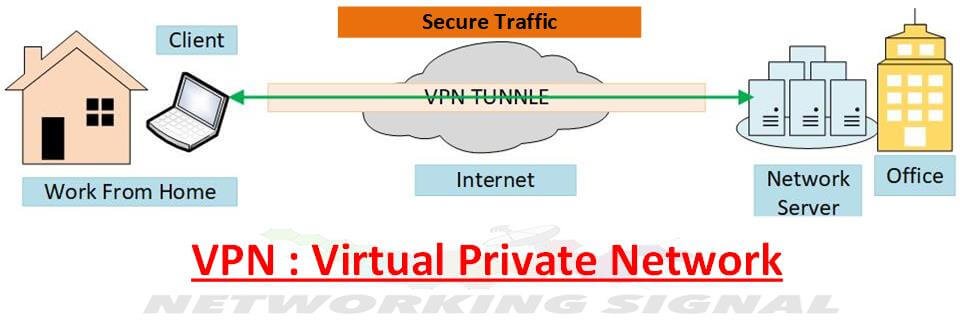
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a private network that encrypts and transmits data while it travels from one place to another. A VPN is created by establishing a virtual point-to-point connection through the use of dedicated connections, virtual tunneling protocols, or traffic encryption.
A VPN available from the public Internet can provide some of the benefits of a wide area network (WAN). From a user perspective, the resources available within the private network can be accessed remotely.
Most VPNs are implemented with tunneling protocols such as Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) or Internet Protocol Security (IPsec). These protocols can be used in combination with Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) to create a highly secure VPN.
To understand the importance of VPNs, exploring the benefits of a VPN free test becomes essential. These trials allow organizations to assess the effectiveness of VPN services before making informed decisions, ensuring enhanced security and efficient operations.
This article delves into the fundamental aspects of VPNs, types, advantages, and how VPNs are important in an organization.
Types of VPN
There are two types of VPNs:
Remote-access VPN: A remote-access VPN allows a user to connect to a private network from anywhere in the world. The user first establishes a connection with a remote access server (RAS), typically located at the customer’s premises. The user then authenticates with the RAS and is assigned an IP address. The user can now access the resources of the private network as if he or she were physically connected to it.
Site-to-site VPN: A site-to-site VPN allows users to connect to a private network at multiple locations. Site-to-site VPNs are often used in organizations that have multiple remote offices. The organization can establish a secure connection between each office and the central site. This allows the resources of the private network to be shared among all the locations.
Types of VPN Protocols
There are several different types of VPN protocols, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP): PPTP is a legacy VPN protocol that is still used by many organizations. It uses a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) to encapsulate data. PPTP has been superseded by more secure VPN protocols such as L2TP/IPsec and IKEv2/IPsec.
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP): L2TP is a more recent VPN protocol that combines the best features of PPTP and Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F). L2TP uses UDP port 1701.
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec): IPSec is a standards-based VPN protocol that has been implemented in a number of products. It uses strong encryption and can be used in combination with other protocols such as L2TP.
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL): SSL is a VPN protocol that uses the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to provide security. SSL is commonly used by web browsers to provide a secure connection.
OpenVPN: OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol that uses SSL/TLS for key exchange. It can be used with a variety of encryption algorithms.
Advantages of VPN
There are several advantages of using a VPN:
Security: VPNs provide a high level of security through encryption and other security mechanisms. This makes it difficult for anyone to eavesdrop on data being transmitted over the VPN.
Cost: VPNs can be much cheaper than traditional leased lines.
Flexibility: VPNs can be used to connect remote offices, mobile workers, and home users.
Scalability: VPNs can be easily scaled to accommodate the needs of a growing organization.
Availability: VPNs can be used to provide always-on connectivity.
How VPN is Important for an Organization?
An organization can use a VPN to connect to the Internet in a secure and cost-effective manner. A VPN can also be used to connect to internal resources such as file servers, printers, and email servers. This allows an organization to provide its employees with access to these resources from anywhere in the world.
A VPN can also be used to connect an organization’s branches to each other. This allows the sharing of resources such as files and printers. It also allows employees in different locations to communicate with each other using VoIP (Voice over IP) or video conferencing.
A VPN can be used to provide a high level of security for an organization’s data. All data transmitted over the VPN is encrypted, making it difficult for anyone to eavesdrop on the traffic.
A VPN can also be used to authenticate users before they are granted access to resources. This helps to ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive information.
VPNs are an important part of an organization’s infrastructure and can be used to provide many benefits. They are relatively easy to deploy and can be used to connect an organization’s employees, branches, and partners in a secure and cost-effective manner.
What is the Compatibility of VPN?
VPNs are compatible with a variety of operating systems and devices. Most VPNs use the IPsec protocol and can be used with a variety of products such as Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and routers.

