What is a Wide Area Network?
A wide area network (WAN) is a large, distributed computer network that typically spans multiple geographical locations. A WAN often uses public networks, such as the Internet, to connect to smaller private networks, such as a local area network (LAN). WANs are used to connect LANs and other types of networks together so that they can communicate with each other.
What are the Methods of Wide Area Network Connectivity?
There are three primary ways to connect a wide area network:
- point-to-point
- circuit switching
- packet switching
Point-to-point connections are the simplest form of WAN connectivity. They consist of two devices that are connected directly to each other using a physical medium, such as a copper wire or fiber optic cable. Point-to-point connections are typically used to connect two devices close to each other, such as two computers in the same room.
Circuit switching is a method of connecting WAN devices in which a dedicated circuit is established between the two devices for the duration of the connection. The circuit is analogous to a telephone line, in that it is a physical connection that can be used to transmit data in both directions. Circuit switching is typically used to connect devices that are located at a considerable distance from each other, such as two computers in different buildings.
Packet switching is a method of connecting WAN devices in which data is divided into small packets that are transmitted independently of each other over a shared medium, such as a copper wire or fiber optic cable. Packet switching is the most common form of WAN connectivity and is used to connect devices that are located at a considerable distance from each other, such as two computers in different buildings.
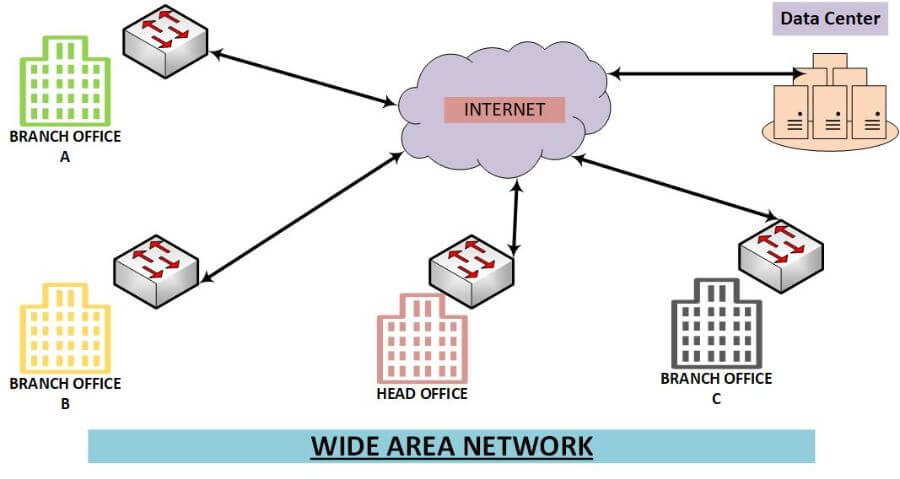
What are the Advantages of Wide Area Networks?
Here are some advantages of using a WAN:
- WANs can connect devices that are located at a considerable distance from each other.
- WANs can be used to connect multiple LANs together.
- WANs can be used to connect devices that use different types of networking protocols.
- WANs are typically more reliable than LANs.
- WANs can be used to connect devices that use different types of networking hardware.
What are the Disadvantages of Wide Area Networks?
There are also some disadvantages to using a WAN:
- WANs can be expensive to set up and maintain.
- WANs can be complex to configure and troubleshoot.
- WANs can be vulnerable to security breaches.
- WANs can be susceptible to network congestion.
- WANs can be disrupted by natural disasters.
How does Media Access Work Via WAN?
There are three primary types of media access control:
- contention-based
- token-based
- polling-based
Contention-based media access control is the most common type of media access control used in WANs. It is a simple method in which each device on the network competes for the right to use the medium. The device that wins the right to use the medium transmits its data, and then the process repeats itself.
Token-based media access control is a more sophisticated method in which each device on the network is assigned a unique token. The device that possesses the token has the right to use the medium, and it can pass the token to another device when it is finished using the medium.
Polling-based media access control is a method in which each device on the network is assigned a unique address. The controller of the network periodically polls each device to see if it has data to transmit. If the device has data to communicate, it transmits its data and then the process repeats itself.
How does Transmission Work Via WAN?
There are two primary types of transmission:
- analog
- digital
Analog transmission is a type of transmission in which the data is represented by a continuously variable signal. Analog transmission is typically used for voice communication because it can reproduce the full range of human speech.
Digital transmission is a type of transmission in which the data is represented by a discrete signal. Digital transmission is typically used for data communication because it can transmit data more accurately than analog transmission.
What are the Types of WAN Connections?
There are two primary types of WAN connections:
- dedicated
- shared
Dedicated connections are permanent connections that are used exclusively by a single organization.
Shared connections are temporary connections that multiple organizations use.
Where We Can Use WANs?
WANs can be used to connect devices that are located in the same room, such as two computers, or they can be used to connect devices that are located in different buildings, such as a computer and a printer. WANs can also be used to connect devices that are located in different countries, such as a computer in the United States and a computer in Japan.
Wide Area Network Protocols
The most common type of WAN protocol is the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). TCP/IP is a set of protocols that are used to transmit data over a network. TCP/IP is the standard protocol for data communication on the Internet.
Other common WAN protocols include:
- Frame Relay
- ATM
- X.25
Frame relay is a type of data link layer protocol that is used to transmit data over a network. Frame relay is typically used for voice and video communication.
ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) is a type of packet-based switching technology that is used to transmit data over a network. ATM is typically used for high-speed data communication.
X.25 is a type of packet-switching technology that is used to transmit data over a network. X.25 is typically used for voice and video communication.
Wide Area Network Applications
There are a variety of applications that can be used with a wide area network. These applications can be divided into two categories:
1. Public switched telephone network (PSTN) applications include:
- Voice telephony
- Fax
- Text messaging
- Pager services
- Voice mail
2. Internet applications include:
- World Wide Web
- File transfer
- Streaming media
- Voice over IP (VoIP)
- Video conferencing
- Instant messaging
What is the Future of WANs?
The future of wide-area networks is likely to be dominated by two trends:
1. The increasing use of packet-based technologies such as ATM and IP
Packet-based technologies offer a number of advantages over traditional circuit-based technologies, including:
- Increased flexibility
- Increased efficiency
- Reduced costs
- Reduced complexity
- Increased scalability
- Improved performance
- Enhanced security
- Improved manageability
- Increased reliability
- Greater interoperability
- Support for new applications and services
2. The increasing use of optical fiber technologies such as SONET and DWDM
Optical fiber technologies offer a number of advantages over traditional copper-based technologies, including:
- Increased bandwidth
- Reduced costs
- Increased scalability
- Improved performance
- Enhanced security
- Increased reliability
- Greater interoperability
- Support for new applications and services

