What is Site To Site VPN?
Site-to-site VPN is a VPN connection that allows two or more remote sites to share a common network. This type of VPN is commonly used in large organizations that have multiple office locations. By using a Site To Site VPN, these organizations can connect their various offices together and allow employees to share files and other resources. Site-to-site VPNs can also be used to connect two or more different companies together.
There are two main types of Site to Site VPNs
- point to point
- multipoint
Point-to-point VPNs are the simplest type of site-to-site VPN and involve two routers, each with a single connection to the other. Multipoint VPNs, on the other hand, involve multiple routers with multiple connections to each other.
What is Azure Site-to-Site VPN?
Azure Site-to-Site VPN is a type of virtual private network (VPN) connection that allows organizations to securely connect their on-premise networks to Microsoft Azure.
It establishes a secure connection between an Azure Virtual Network and the customer’s on-premises IT infrastructure by providing an encrypted tunnel across the public Internet.
Organizations can use Site-to-Site VPNs to securely share resources, applications, and data between on-premises and Azure Virtual Networks.
What is Unifi Site-to-Site VPN?
Unifi Site-to-Site VPN is a feature of Ubiquiti’s Unifi line of gateway devices that allows organizations to securely connect their on-premise networks with remote locations over the public Internet.
The Unifi Site-to-Site VPN creates a secure tunnel between two Unifi gateways (one on-premise and one remote) for data to pass through. It is an ideal solution for distributed organizations with remote offices or partners that need a secure connection to access resources on-premise.
The Unifi Site-to-Site VPN also supports multiple topologies such as road warrior, hub and spoke, and full mesh networking.
What is Meraki Site-to-Site VPN?
Meraki Site-to-Site VPN is a secure connection between an on-premise Meraki network and a remote site or location. It enables organizations to deploy applications, access resources, and extend their corporate networks to branch offices, retail outlets, field service technicians, and more.
With Meraki’s cloud-managed platform, setting up a Site-to-Site VPN is simple and requires minimal configuration. The connection is always secure and encrypted, allowing the organization to securely access the remote site or location without having to worry about network security.
Meraki Site-to-Site VPN also provides dynamic routing protocols (such as RIP and OSPF) that make it easy to establish a point-to-point link between two networks.
What is Fortigate Site-to-Site VPN?
Fortigate Site to Site VPN is a type of VPN connection that allows organizations to securely connect their Fortigate firewall devices with Microsoft Azure using an encrypted tunnel across the public internet.
The connection provides secure access between the on-premise network and the Azure Virtual Network and allows organizations to share resources, applications, and data between on-premises and Azure.
The Fortigate Site-to-Site VPN is easy to configure, cost-effective and reliable. It provides organizations with a secure way to connect their on-premise networks with Azure without the need for additional hardware or software.
What are the Advantages of Site-to-Site VPN?
There are several advantages to using a site-to-site VPN:
- Increased security: A site-to-site VPN help to improve network security. Using a VPN, all data sent between the two sites is encrypted. This makes it much more difficult for anyone to intercept and read the data.
- Improved performance: A VPN can help improve the performance of a network by reducing the amount of traffic that needs to be sent over the public internet.
- Flexibility: A VPN can be used to connect two sites that are far apart, or it can be used to connect a site to the internet.
What are the Disadvantages of Site To Site VPN?
There are also some disadvantages to using a site-to-site VPN:
- Cost: A site-to-site VPN can be more expensive to set up and maintain than other types of VPNs.
- Complexity: Site-to-site VPNs can be complex to set up and manage, especially if multiple sites are involved.
- Limited compatibility: Some types of site-to-site VPNs may not be compatible with all types of devices and networks.
How Site-to-Site VPN Works?
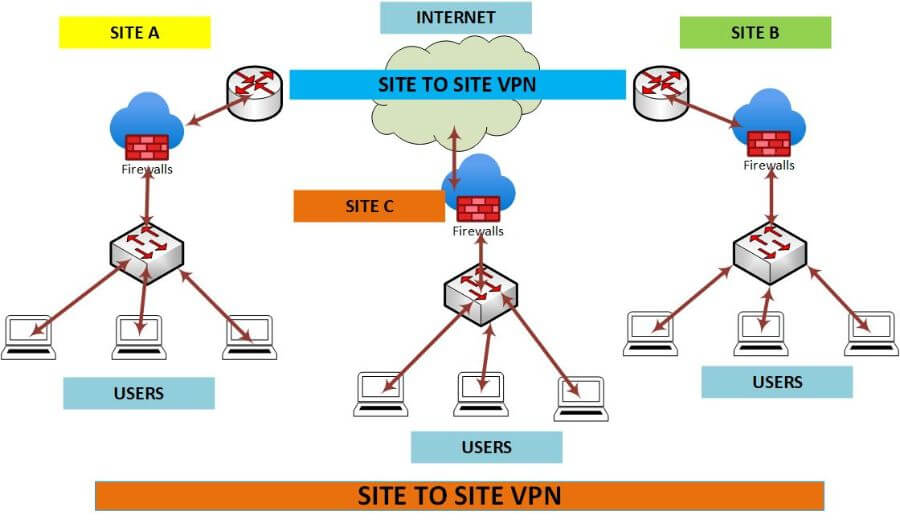
A site-to-site VPN typically involves two routers, each with a connection to the other. The first router is connected to the internet, and the second router is connected to the first router. Data that is sent between the two routers is encrypted, so it cannot be read by anyone who intercepts it.
Where We Can Use Site-to-Site VPN?
Site-to-site VPNs can be used in a variety of situations, including:
- Connecting two or more office locations together
- Connecting a remote office to a central network
- Connecting two or more companies together
- Connecting a branch office to a central network